Placental pathology and neonatal encephalopathy
- PMID: 35694848
- PMCID: PMC10084103
- DOI: 10.1002/ijgo.14301
Placental pathology and neonatal encephalopathy
Abstract
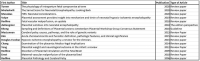
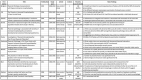
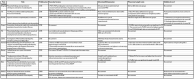
Neonatal encephalopathy (NE) is an important cause of neonatal morbidity and mortality worldwide; however, there remain gaps in our knowledge about its pathogenesis. The placenta has been implicated in the pathogenesis of this disease but conclusive evidence related to the placental factors that influence it is sparse. This review aims to outline the current knowledge on the role of the placenta with particular attention to its role in NE as a consequence of hypoxia-ischemia. A total of 26 original articles/review papers were used to compile this review. Three themes were identified from these publications: fetal vascular malperfusion including umbilical cord pathology, inflammatory changes in the placenta, and maternal vascular malperfusion including placental weight. These features were identified as being significant in the development of NE. Advancing our understanding of this relationship between placental pathology and NE may facilitate the development of additional antenatal screening to better identify at-risk fetuses. We highlight areas for further research through antenatal screening and placental histology.
Keywords: cerebral palsy; fetal vascular malperfusion; hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; neonatal encephalopathy; placenta.
© 2022 The Authors. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- McDonald DG, Kelehan P, McMenamin JB, et al. Placental fetal thrombotic vasculopathy is associated with neonatal encephalopathy. Hum Pathol. 2004;35(7):875‐880. - PubMed
-
- Vik T, Redline R, Nelson KB, et al. The placenta in neonatal encephalopathy: a case‐control study. J Pediatr. 2018;202:77‐85.e3. - PubMed
-
- Nasiell J, Papadogiannakis N, Löf E, et al. Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy in newborns linked to placental and umbilical cord abnormalities. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29(5):721‐726. - PubMed
-
- Douglas‐Escobar M, Weiss MD. Hypoxic‐ischemic encephalopathy: a review for the clinician. JAMA Pediatr. 2015;169(4):397‐403. - PubMed
-
- Turner JM, Mitchell MD, Kumar SS. The physiology of intrapartum fetal compromise at term. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;222(1):17‐26. - PubMed