INCEPTUS Natural History, Run-in Study for Gene Replacement Clinical Trial in X-Linked Myotubular Myopathy
- PMID: 35694931
- PMCID: PMC9398079
- DOI: 10.3233/JND-210781
INCEPTUS Natural History, Run-in Study for Gene Replacement Clinical Trial in X-Linked Myotubular Myopathy
Abstract
Background: X-linked myotubular myopathy (XLMTM) is a life-threatening congenital myopathy that, in most cases, is characterized by profound muscle weakness, respiratory failure, need for mechanical ventilation and gastrostomy feeding, and early death.
Objective: We aimed to characterize the neuromuscular, respiratory, and extramuscular burden of XLMTM in a prospective, longitudinal study.
Methods: Thirty-four participants < 4 years old with XLMTM and receiving ventilator support enrolled in INCEPTUS, a prospective, multicenter, non-interventional study. Disease-related adverse events, respiratory and motor function, feeding, secretions, and quality of life were assessed.
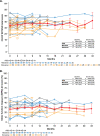
Results: During median (range) follow-up of 13.0 (0.5, 32.9) months, there were 3 deaths (aspiration pneumonia; cardiopulmonary failure; hepatic hemorrhage with peliosis) and 61 serious disease-related events in 20 (59%) participants, mostly respiratory (52 events, 18 participants). Most participants (80%) required permanent invasive ventilation (>16 hours/day); 20% required non-invasive support (6-16 hours/day). Median age at tracheostomy was 3.5 months (95% CI: 2.5, 9.0). Thirty-three participants (97%) required gastrostomy. Thirty-one (91%) participants had histories of hepatic disease and/or prospectively experienced related adverse events or laboratory or imaging abnormalities. CHOP INTEND scores ranged from 19-52 (mean: 35.1). Seven participants (21%) could sit unsupported for≥30 seconds (one later lost this ability); none could pull to stand or walk with or without support. These parameters remained static over time across the INCEPTUS cohort.
Conclusions: INCEPTUS confirmed high medical impact, static respiratory, motor and feeding difficulties, and early death in boys with XLMTM. Hepatobiliary disease was identified as an under-recognized comorbidity. There are currently no approved disease-modifying treatments.
Keywords: X-linked myotubular myopathy; centronuclear myopathy; mechanical; motor disorders; neuromuscular diseases; respiratory failure; ventilators.
Conflict of interest statement
JJD reports research grants from Astellas Gene Therapies,* serving on advisory boards for Dynacure, Kate Therapeutics, and RYR1 Foundation, and serving as an editor of the
*Formerly Audentes Therapeutics
Figures

References
-
- Laporte J, Biancalana V, Tanner SM, Kress W, Schneider V, Wallgren-Pettersson C, et al.. MTM1 mutations in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Hum Mutat. 2000;15(5):393–409. - PubMed
-
- Herman GE, Finegold M, Zhao W, de Gouyon B, Metzenberg A. Medical complications in long-term survivors with X-linked myotubular myopathy. J Pediatr. 1999;134(2):206–14. - PubMed
-
- McEntagart M, Parsons G, Buj-Bello A, Biancalana V, Fenton I, Little M, et al.. Genotype-phenotype correlations in X-linked myotubular myopathy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2002;12(10):939–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

