Extract of Pinus densiflora needles suppresses acute inflammation by regulating inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 macrophages and mice
- PMID: 35695008
- PMCID: PMC9196672
- DOI: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2079679
Extract of Pinus densiflora needles suppresses acute inflammation by regulating inflammatory mediators in RAW264.7 macrophages and mice
Abstract
Context: Pinus densiflora Siebold & Zucc. (Pinaceae) needle extracts ameliorate oxidative stress, but research into their anti-inflammatory effects is limited.
Objective: To investigate antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of a Pinus densiflora needles (PINE) ethanol extract in vitro and in vivo.
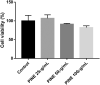
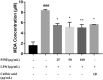
Materials and methods: We measured levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 cells at various PINE concentrations (25, 50 and 100 μg/mL; but 6.25, 12.5 and 25 μg/mL for interleukin-1β and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2)). Thirty ICR mice were randomized to six groups: vehicle, control, PINE pre-treatment (0.1, 0.3 and 1 mg/left ear for 10 min followed by arachidonic acid treatment for 30 min) and dexamethasone. The posttreatment ear thickness and myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity were measured.
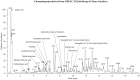
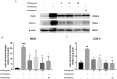
Results: PINE 100 μg/mL significantly decreased ROS (IC50, 70.93 μg/mL, p < 0.01), SOD (IC50, 30.99 μg/mL, p < 0.05), malondialdehyde (p < 0.01), nitric oxide (NO) (IC50, 27.44 μg/mL, p < 0.01) and tumour necrosis factor-alpha (p < 0.05) levels. Interleukin-1β (p < 0.05) and PGE2 (p < 0.01) release decreased significantly with 25 μg/mL PINE. PINE 1 mg/ear inhibited LPS-stimulated expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible NO synthase in RAW264.7 macrophages and significantly inhibited ear oedema (36.73-15.04% compared to the control, p < 0.01) and MPO activity (167.94-105.59%, p < 0.05).
Discussion and conclusions: PINE exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting the production of inflammatory mediators. Identified flavonoids such as taxifolin and quercetin glucoside can be attributed to effect of PINE.
Keywords: Reactive oxygen species; anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; arachidonic acid; ear oedema; lipopolysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pinus densiflora needle supercritical fluid extract suppresses the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators iNOS, IL-6 and IL-1β, and activation of inflammatory STAT1 and STAT3 signaling proteins in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-challenged murine macrophages.Daru. 2017 Aug 4;25(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s40199-017-0184-y. Daru. 2017. PMID: 28778215 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory properties of fermented pine (Pinus morrisonicola Hay.) needle on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.J Food Biochem. 2019 Nov;43(11):e12994. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.12994. Epub 2019 Jul 28. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31659812
-
Ethyl acetate fraction from Nymphaea hybrida Peck modulates inflammatory responses in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells and acute inflammation murine models.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113698. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113698. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33338590
-
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Effects of Korean Ginseng Berry Extract in LPS-Activated RAW264.7 Macrophages.Am J Chin Med. 2021;49(3):719-735. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X21500336. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Am J Chin Med. 2021. PMID: 33683191
-
Pinus Species as Prospective Reserves of Bioactive Compounds with Potential Use in Functional Food-Current State of Knowledge.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jun 28;10(7):1306. doi: 10.3390/plants10071306. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Therapeutic Potentials of Taxifolin for Obesity-Induced Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrogenesis, and Tumorigenesis.Nutrients. 2023 Jan 10;15(2):350. doi: 10.3390/nu15020350. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 36678220 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids in lung cancer: Navigating the balance between immunosuppression and therapeutic efficacy.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 4;10(12):e32357. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32357. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and inflammation: natural product-derived treatments-a review of the last ten years.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Dec;31(6):2939-2954. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01339-1. Epub 2023 Sep 23. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37740887 Review.
-
Anti-Amnesia-like Effect of Pinus densiflora Extract by Improving Apoptosis and Neuroinflammation on Trimethyltin-Induced ICR Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 14;24(18):14084. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814084. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abou-zaid MM, Nozzolillo C.. 1991. Flavonol glycosides from needles of Pinus banksiana. Biochem Syst Ecol. 19(3):1148–240.
-
- Ahn H, Go GW.. 2017. Pinus densiflora bark extract (PineXol) decreases adiposity in mice by down-regulation of hepatic de novo lipogenesis and adipogenesis in white adipose tissue. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 27(4):660–667. - PubMed
-
- Akundi RS, Candelario-Jalil E, Hess S, Hüll M, Lieb K, Gebicke-Haerter PJ, Fiebich BL.. 2005. Signal transduction pathways regulating cyclooxygenase-2 in lipopolysaccharide-activated primary rat microglia. Glia. 51(3):199–208. - PubMed
-
- Ascari J, de Oliveira MS, Nunes DS, Granato D, Scharf DR, Simionatto E, Otuki M, Soley B, Heiden G.. 2019. Chemical composition, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of the essential oils from male and female specimens of Baccharis punctulata (Asteraceae). J Ethnopharmacol. 234:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Barragán-Zarate GS, Lagunez-Rivera L, Solano R, Pineda-Peña EA, Landa-Juárez AY, Chávez-Piña AE, Carranza-Álvarez C, Hernández-Benavides DM.. 2020. Prosthechea karwinskii, an orchid used as traditional medicine, exerts anti-inflammatory activity and inhibits ROS. J Ethnopharmacol. 253:112632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
