The evolution and structure/function of bHLH-PAS transcription factor family
- PMID: 35695677
- PMCID: PMC10584024
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20211225
The evolution and structure/function of bHLH-PAS transcription factor family
Abstract
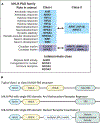
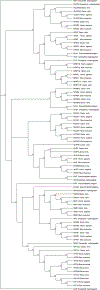
Proteins that contain basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) and Per-Arnt-Sim motifs (PAS) function as transcription factors. bHLH-PAS proteins exhibit essential and diverse functions throughout the body, from cell specification and differentiation in embryonic development to the proper function of organs like the brain and liver in adulthood. bHLH-PAS proteins are divided into two classes, which form heterodimers to regulate transcription. Class I bHLH-PAS proteins are typically activated in response to specific stimuli, while class II proteins are expressed more ubiquitously. Here, we discuss the general structure and functions of bHLH-PAS proteins throughout the animal kingdom, including family members that do not fit neatly into the class I-class II organization. We review heterodimerization between class I and class II bHLH-PAS proteins, binding partner selectivity and functional redundancy. Finally, we discuss the evolution of bHLH-PAS proteins, and why a class I protein essential for cardiovascular development in vertebrates like chicken and fish is absent from mammals.
Keywords: aryl hydrocarbon receptor; bHLH–PAS transcription factors; hypoxia inducible factors; signalling; transcription.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Portland Press Limited on behalf of the Biochemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

