Traditional Vietnamese medicine Kovir capsule in patients with mild COVID-19: A double-blind randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35695687
- PMCID: PMC9349637
- DOI: 10.1002/ptr.7455
Traditional Vietnamese medicine Kovir capsule in patients with mild COVID-19: A double-blind randomized controlled trial
Abstract
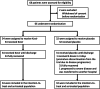
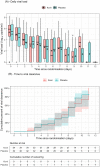
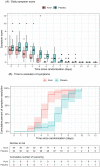
Kovir capsule, a polyherbal medicine developed from Ren Shen Bai Du San formulation, has been used in various diseases including respiratory infections. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study was conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Kovir capsule (TD0069) in the treatment of mild COVID-19 patients. Patients aged from 18 to 65 years who were PCR-confirmed with SARS-CoV-2 and had the mild disease were recruited and randomized to either Kovir capsule (34 patients) or placebo (32 patients) for up to 14 days or until discharge. Efficacy outcomes were time to viral clearance, daily viral load, time to symptom resolution, daily symptom score based on 16 pre-defined symptoms, and progression to severe/critical COVID-19. Safety outcomes were adverse events. Viral load decreased over time similarly in the two groups. Viral clearance time was also similar in both groups (median: 8 days). Kovir group had a more rapid decrease of symptom score and significantly lower time to symptom resolution than placebo (median: 4 vs. 7 days). Two patients in the placebo group developed severe COVID-19. No patient experienced adverse events. Kovir capsule is safe and can improve symptom resolution in mild COVID-19 patients. A large-scale trial is required to confirm these findings.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; herbal; traditional medicine.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors confirm that they have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Chen, J. K. , & Chen, T. T. (2009). Chinese herbal formulas and applications: Pharmacological effects & clinical research. City of industry, CA: Art of Medicine Press.
-
- Devpura, G. , Tomar, B. S. , Nathiya, D. , Sharma, A. , Bhandari, D. , Haldar, S. , … Varshney, A. (2021). Randomized placebo‐controlled pilot clinical trial on the efficacy of ayurvedic treatment regime on COVID‐19 positive patients. Phytomedicine, 84, 153494. 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153494 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grifoni, A. , Weiskopf, D. , Ramirez, S. I. , Mateus, J. , Dan, J. M. , Moderbacher, C. R. , … Sette, A. (2020). Targets of T cell responses to SARS‐CoV‐2 coronavirus in humans with COVID‐19 disease and unexposed individuals. Cell, 181(7), 1489–1501.e1415. 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

