Outcomes of culture-negative vs. culture-positive infective endocarditis: the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO registry
- PMID: 35695691
- PMCID: PMC9459867
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac307
Outcomes of culture-negative vs. culture-positive infective endocarditis: the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO registry
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Outcomes of culture-negative vs. culture-positive infective endocarditis: the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO registry.Eur Heart J. 2023 Jun 1;44(21):1909. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad222. Eur Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37052587 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aim: Fatality of infective endocarditis (IE) is high worldwide, and its diagnosis remains a challenge. The objective of the present study was to compare the clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with culture-positive (CPIE) vs. culture-negative IE (CNIE).
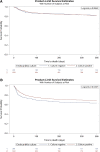
Methods and results: This was an ancillary analysis of the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO registry. Overall, 3113 patients who were diagnosed with IE during the study period were included in the present study. Of these, 2590 (83.2%) had CPIE, whereas 523 (16.8%) had CNIE. As many as 1488 (48.1%) patients underwent cardiac surgery during the index hospitalization, 1259 (48.8%) with CPIE and 229 (44.5%) with CNIE. The CNIE was a predictor of 1-year mortality [hazard ratio (HR) 1.28, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.04-1.56], whereas surgery was significantly associated with survival (HR 0.49, 95% CI 0.41-0.58). The 1-year mortality was significantly higher in CNIE than CPIE patients in the medical subgroup, but it was not significantly different in CNIE vs. CPIE patients who underwent surgery.
Conclusion: The present analysis of the EURO-ENDO registry confirms a higher long-term mortality in patients with CNIE compared with patients with CPIE. This difference was present in patients receiving medical therapy alone and not in those who underwent surgery, with surgery being associated with reduced mortality. Additional efforts are required both to improve the aetiological diagnosis of IE and identify CNIE cases early before progressive disease potentially contraindicates surgery.
Keywords: Blood culture-negative endocarditis; Diagnosis; Endocarditis; Heart valves; Infective endocarditis; Surgery.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Comment in
-
A double negative: culture-negative infective endocarditis.Eur Heart J. 2022 Aug 1;43(29):2781-2782. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac230. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 35678590 No abstract available.
References
-
- Habib G, Erba PA, Iung B, Donal E, Cosyns B, Laroche C, et al. . Clinical presentation, aetiology and outcome of infective endocarditis. Results of the ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO (European Infective Endocarditis) registry: a prospective cohort study. Eur Heart J 2019; 40:3222–3232. - PubMed
-
- Habib G, Lancellotti P, Erba PA, Sadeghpour A, Meshaal M, Sambola A, et al. . The ESC-EORP EURO-ENDO (European Infective Endocarditis) registry. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes 2019;5:202–207. - PubMed
-
- Charlson M, Szatrowski TP, Peterson J, Gold J. Validation of a combined comorbidity index. J Clin Epidemiol 1994;47:1245–1251. - PubMed
-
- Habib G, Lancellotti P, Antunes MJ, Bongiorni MG, Casalta JP, Del Zotti F, et al. . 2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of infective endocarditis: the task force for the management of infective endocarditis of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Endorsed by: European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS), the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM). Eur Heart J 2015;36:3075–3128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

