Haplotype-resolved powdery mildew resistance loci reveal the impact of heterozygous structural variation on NLR genes in Muscadinia rotundifolia
- PMID: 35695769
- PMCID: PMC9339307
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac148
Haplotype-resolved powdery mildew resistance loci reveal the impact of heterozygous structural variation on NLR genes in Muscadinia rotundifolia
Abstract
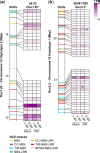
Muscadinia rotundifolia cv. Trayshed is a valuable source of resistance to grape powdery mildew. It carries 2 powdery mildew resistance-associated genetic loci, Run1.2 on chromosome 12 and Run2.2 on chromosome 18. The purpose of this study was to identify candidate resistance genes associated with each haplotype of the 2 loci. Both haplotypes of each resistance-associated locus were identified, phased, and reconstructed. Haplotype phasing allowed the identification of several structural variation events between haplotypes of both loci. Combined with a manual refinement of the gene models, we found that the heterozygous structural variants affected the gene content, with some resulting in duplicated or hemizygous nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat genes. Heterozygous structural variations were also found to impact the domain composition of some nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat proteins. By comparing the nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat proteins at Run1.2 and Run2.2 loci, we discovered that the 2 loci include different numbers and classes of nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat genes. To identify powdery mildew resistance-associated genes, we performed a gene expression profiling of the nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat genes at Run1.2b and Run2.2 loci with or without powdery mildew present. Several nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat genes were constitutively expressed, suggesting a role in powdery mildew resistance. These first complete, haplotype-resolved resistance-associated loci and the candidate nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat genes identified by this study are new resources that can aid the development of powdery mildew-resistant grape cultivars.
Keywords: genetic resistance; genomic structural variation; haplotype phasing; nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat genes.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures



References
-
- Barker CL, Donald T, Pauquet J, Ratnaparkhe MB, Bouquet A, Adam-Blondon AF, Thomas MR, Dry I.. Genetic and physical mapping of the grapevine powdery mildew resistance gene, Run1, using a bacterial artificial chromosome library. Theor Appl Genet. 2005;111(2):370–377. - PubMed
-
- Cingolani P, Platts A, Wang le L, Coon M, Nguyen T, Wang L, Land SJ, Lu X, Ruden DM.. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster strain w1118; iso-2; iso-3. Fly (Austin). 2012;6(2):80–92. - PMC - PubMed
