Evolution of the DEHYDRATION-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT-BINDING PROTEIN subfamily in green plants
- PMID: 35695786
- PMCID: PMC9434268
- DOI: 10.1093/plphys/kiac286
Evolution of the DEHYDRATION-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT-BINDING PROTEIN subfamily in green plants
Abstract
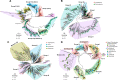
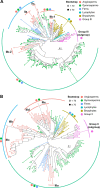
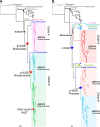
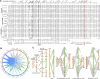
Adapting to unfavorable environments is a necessary step in plant terrestrialization and radiation. The dehydration-responsive element-binding (DREB) protein subfamily plays a pivotal role in plant abiotic stress regulation. However, relationships between the origin and expansion of the DREB subfamily and adaptive evolution of land plants are still being elucidated. Here, we constructed the evolutionary history of the DREB subfamily by compiling APETALA2/ethylene-responsive element-binding protein superfamily genes from 169 representative species of green plants. Through extensive phylogenetic analyses and comparative genomic analysis, our results revealed that the DREB subfamily diverged from the ethylene-responsive factor (ERF) subfamily in the common ancestor of Zygnemophyceae and Embryophyta during the colonization of land by plants, followed by expansions to form three different ancient archetypal genes in Zygnemophyceae species, designated as groups archetype-I, archetype-II/III, and archetype-IV. Four large-scale expansions paralleling the evolution of land plants led to the nine-subgroup divergence of group archetype-II/III in angiosperms, and five whole-genome duplications during Brassicaceae and Poaceae radiation shaped the diversity of subgroup IIb-1. We identified a Poaceae-specific gene in subgroup IIb-1, ERF014, remaining in a Poaceae-specific microsynteny block and co-evolving with a small heat shock protein cluster. Expression analyses demonstrated that heat acclimation may have driven the neofunctionalization of ERF014s in Pooideae by engaging in the conserved heat-responsive module in Poaceae. This study provides insights into lineage-specific expansion and neofunctionalization in the DREB subfamily, together with evolutionary information valuable for future functional studies of plant stress biology.
© American Society of Plant Biologists 2022. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ancient Duplication and Lineage-Specific Transposition Determine Evolutionary Trajectory of ERF Subfamily across Angiosperms.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 1;25(7):3941. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073941. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612750 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of RLSB, a nuclear-encoded S1 domain RNA binding protein associated with post-transcriptional regulation of plastid-encoded rbcL mRNA in vascular plants.BMC Evol Biol. 2016 Jun 29;16(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12862-016-0713-1. BMC Evol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27356975 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion and stress responses of the AP2/EREBP superfamily in cotton.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 31;18(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-3517-9. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28143399 Free PMC article.
-
The DREB transcription factor, a biomacromolecule, responds to abiotic stress by regulating the expression of stress-related genes.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jul 15;243:125231. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125231. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37301338 Review.
-
Dehydration responsive element binding transcription factors and their applications for the engineering of stress tolerance.J Exp Bot. 2017 Apr 1;68(9):2135-2148. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx118. J Exp Bot. 2017. PMID: 28419345 Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Roles of the GRF Transcription Factors in Sorghum Internodes during Post-Reproductive Stages.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 23;13(17):2352. doi: 10.3390/plants13172352. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273836 Free PMC article.
-
An omics strategy increasingly improves the discovery of genetic loci and genes for seed-coat color formation in soybean.Mol Breed. 2023 Aug 31;43(9):71. doi: 10.1007/s11032-023-01414-z. eCollection 2023 Sep. Mol Breed. 2023. PMID: 37663546 Free PMC article.
-
Pan-Genome Analysis Reveals Local Adaptation to Climate Driven by Introgression in Oak Species.Mol Biol Evol. 2025 Apr 30;42(5):msaf088. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaf088. Mol Biol Evol. 2025. PMID: 40235155 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient Duplication and Lineage-Specific Transposition Determine Evolutionary Trajectory of ERF Subfamily across Angiosperms.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 1;25(7):3941. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073941. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal PK, Gupta K, Lopato S, Agarwal P (2017) Dehydration responsive element binding transcription factors and their applications for the engineering of stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 68: 2135–2148 - PubMed
-
- Appels R, Eversole K, Feuillet C, Keller B, Rogers J, Stein N, Pozniak CJ, Stein N, Choulet F, Distelfeld A, et al. (2018) Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science 361: eaar7191. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

