Fast-Forming Dissolvable Redox-Responsive Hydrogels: Exploiting the Orthogonality of Thiol-Maleimide and Thiol-Disulfide Exchange Chemistry
- PMID: 35696518
- PMCID: PMC9472223
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.2c00209
Fast-Forming Dissolvable Redox-Responsive Hydrogels: Exploiting the Orthogonality of Thiol-Maleimide and Thiol-Disulfide Exchange Chemistry
Abstract
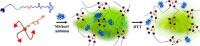
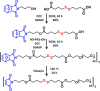
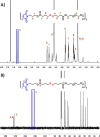
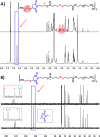
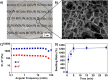
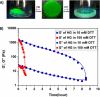
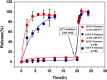
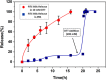
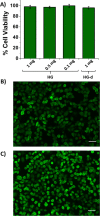
Fast-forming yet easily dissolvable hydrogels (HGs) have potential applications in wound healing, burn incidences, and delivery of therapeutic agents. Herein, a combination of a thiol-maleimide conjugation and thiol-disulfide exchange reaction is employed to fabricate fast-forming HGs which rapidly dissolve upon exposure to dithiothreitol (DTT), a nontoxic thiol-containing hydrophilic molecule. In particular, maleimide disulfide-terminated telechelic linear poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) polymer and PEG-based tetrathiol macromonomers are employed as gel precursors, which upon mixing yield HGs within a minute. The selectivity of the thiol-maleimide conjugation in the presence of a disulfide linkage was established through 1H NMR spectroscopy and Ellman's test. Rapid degradation of HGs in the presence of thiol-containing solution was evident from the reduction in storage modulus. HGs encapsulated with fluorescent dye-labeled dextran polymers and bovine serum albumin were fabricated, and their cargo release was investigated under passive and active conditions upon exposure to DTT. One can envision that the rapid gelation and fast on-demand dissolution under relatively benign conditions would make these polymeric materials attractive for a range of biomedical applications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Redox-Responsive Hydrogels for Tunable and "On-Demand" Release of Biomacromolecules.Bioconjug Chem. 2022 May 18;33(5):839-847. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00094. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Bioconjug Chem. 2022. PMID: 35446015 Free PMC article.
-
Facile Fabrication of a Modular "Catch and Release" Hydrogel Interface: Harnessing Thiol-Disulfide Exchange for Reversible Protein Capture and Cell Attachment.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018 May 2;10(17):14399-14409. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b00802. Epub 2018 Apr 23. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. PMID: 29637775
-
Stabilization of polymer-hydrogel capsules via thiol-disulfide exchange.Small. 2009 Nov;5(22):2601-10. doi: 10.1002/smll.200900906. Small. 2009. PMID: 19771568
-
Thiolated Polymeric Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications: A Review.Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(40):3172-3186. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666230825100859. Curr Pharm Des. 2023. PMID: 37622704 Review.
-
Thiolated polymeric hydrogels for biomedical application: Cross-linking mechanisms.J Control Release. 2021 Feb 10;330:470-482. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.12.037. Epub 2020 Dec 23. J Control Release. 2021. PMID: 33359581 Review.
Cited by
-
Metal-Free Click-Chemistry: A Powerful Tool for Fabricating Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications.Bioconjug Chem. 2024 Apr 17;35(4):433-452. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.4c00003. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Bioconjug Chem. 2024. PMID: 38516745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly Thermally Conductive Liquid Crystalline Epoxy Resin Vitrimers with Reconfigurable, Shape-Memory, Photo-Thermal, and Closed-Loop Recycling Performance.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Jan;12(3):e2410362. doi: 10.1002/advs.202410362. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39576734 Free PMC article.
-
Disulfide-Cross-Linked Tetra-PEG Gels.Macromolecules. 2024 Mar 25;57(7):3058-3065. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.3c02514. eCollection 2024 Apr 9. Macromolecules. 2024. PMID: 38616809 Free PMC article.
-
Biomimetic strain-stiffening in fully synthetic dynamic-covalent hydrogel networks.Chem Sci. 2023 Apr 13;14(18):4796-4805. doi: 10.1039/d3sc00011g. eCollection 2023 May 10. Chem Sci. 2023. PMID: 37181784 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse reactivity of maleimides in polymer science and beyond.Polym Int. 2025 Apr;74(4):296-306. doi: 10.1002/pi.6715. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Polym Int. 2025. PMID: 40255264
References
-
- Gupta A.; Kowalczuk M.; Heaselgrave W.; Britland S. T.; Martin C.; Radecka I. The Production and Application of Hydrogels for Wound Management: A Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 111, 134–151. 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.12.019. - DOI
-
- Yan X.; Fang W.-W.; Xue J.; Sun T.-C.; Dong L.; Zha Z.; Qian H.; Song Y.-H.; Zhang M.; Gong X.; Lu Y.; He T. Thermoresponsive in Situ Forming Hydrogel with Sol–Gel Irreversibility for Effective Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infected Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10074–10084. 10.1021/acsnano.9b02845. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

