Saliva Diagnostics
- PMID: 35696523
- PMCID: PMC9348814
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-061020-123959
Saliva Diagnostics
Abstract
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death, and early detection of this disease is crucial for increasing survival rates. Although cancer can be diagnosed following tissue biopsy, the biopsy procedure is invasive; liquid biopsy provides an alternative that is more comfortable for the patient. While blood, urine, and cerebral spinal fluid can all be used as a source of liquid biopsy, saliva is an ideal source of body fluid that is readily available and easily collected in the most noninvasive manner. Characterization of salivary constituents in the disease setting provides critical data for understanding pathophysiology and the evaluation of diagnostic potential. The aim of saliva diagnostics is therefore to develop a rapid and noninvasive detection of oral and systemic diseases that could be used together with compact analysis systems in the clinic to facilitate point-of-care diagnostics.
Keywords: circulating biomarkers; saliva exosomics; saliva liquid biopsy; salivaomics; salivary exosomes.
Figures



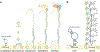
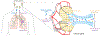
References
-
- Chiappin S, Antonelli G, Gatti R, De Palo EF. 2007. Saliva specimen: a new laboratory tool for diagnostic and basic investigation. Clin. Chim. Acta 383:30–40 - PubMed
-
- Lamy E, Mau M. 2012. Saliva proteomics as an emerging, non-invasive tool to study livestock physiology, nutrition and diseases. J. Proteom 75:4251–58 - PubMed
-
- Carpenter GH. 2013. The secretion, components, and properties of saliva. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol 4:267–76 - PubMed

