Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein regulates the cAMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathway through a positive feedback loop
- PMID: 35696587
- PMCID: PMC9231499
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2121867119
Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein regulates the cAMP-dependent protein kinase signaling pathway through a positive feedback loop
Abstract
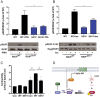
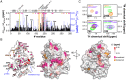
Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein (RKIP) maintains cellular robustness and prevents the progression of diseases such as cancer and heart disease by regulating key kinase cascades including MAP kinase and protein kinase A (PKA). Phosphorylation of RKIP at S153 by Protein Kinase C (PKC) triggers a switch from inhibition of Raf to inhibition of the G protein coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2), enhancing signaling by the β-adrenergic receptor (β-AR) that activates PKA. Here we report that PKA-phosphorylated RKIP promotes β-AR-activated PKA signaling. Using biochemical, genetic, and biophysical approaches, we show that PKA phosphorylates RKIP at S51, increasing S153 phosphorylation by PKC and thereby triggering feedback activation of PKA. The S51V mutation blocks the ability of RKIP to activate PKA in prostate cancer cells and to induce contraction in primary cardiac myocytes in response to the β-AR activator isoproterenol, illustrating the functional importance of this positive feedback circuit. As previously shown for other kinases, phosphorylation of RKIP at S51 by PKA is enhanced upon RKIP destabilization by the P74L mutation. These results suggest that PKA phosphorylation at S51 may lead to allosteric changes associated with a higher-energy RKIP state that potentiates phosphorylation of RKIP at other key sites. This allosteric regulatory mechanism may have therapeutic potential for regulating PKA signaling in disease states.
Keywords: Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein (RKIP); nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); phosphatidylethanolamine binding protein (PEBP); protein kinase A (PKA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

