Hematopoietic stem cell boost for persistent neutropenia after CAR T-cell therapy: a GLA/DRST study
- PMID: 35696759
- PMCID: PMC9984300
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008042
Hematopoietic stem cell boost for persistent neutropenia after CAR T-cell therapy: a GLA/DRST study
Abstract
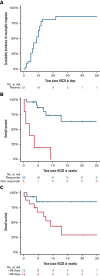
Hematotoxicity after chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is associated with infection and death but management remains unclear. We report results of 31 patients receiving hematopoietic stem cell boost (HSCB; 30 autologous, 1 allogeneic) for either sustained severe neutropenia of grade 4 (<0.5 × 109/L), sustained moderate neutropenia (≤1.5 × 109/L) and high risk of infection, or neutrophil count ≤2.0 × 109/L and active infection. Median time from CAR T-cell therapy to HSCB was 43 days and median absolute neutrophil count at time of HSCB was 0.2. Median duration of neutropenia before HSCB was 38 days (range, 7-151). Overall neutrophil response rate (recovery or improvement) was observed in 26 patients (84%) within a median of 9 days (95% confidence interval, 7-14). Time to response was significantly associated with the duration of prior neutropenia (P = .007). All nonresponders died within the first year after HSCB. One-year overall survival for all patients was 59% and significantly different for neutropenia (≤38 days; 85%) vs neutropenia >38 days before HSCB (44%; P = .029). In conclusion, early or prophylactic HSCB showed quick response and improved outcomes for sustained moderate to severe neutropenia after CAR-T.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: U.H. declares having received honoraria from BMS, Kite Gilead, Miltenyi Biotech, and Novartis. B.v.T. is an advisor or consultant for Allogene, BMS/Celgene, Cerus, Incyte, Miltenyi, Novartis, Pentixafarm, Roche, Amgen, Pfizer, Takeda, Merck Sharp & Dohme, and Gilead Kite. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Fried S, Avigdor A, Bielorai B, et al. Early and late hematologic toxicity following CD19 CAR-T cells. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019;54(10):1643–1650. - PubMed
-
- Bethge WA, Martus P, Schmitt M, et al. GLA/DRST real-world outcome analysis of CAR-T cell therapies for large B-cell lymphoma in Germany. Blood. 2022 blood.2021015209. - PubMed

