Rapid, scalable assessment of SARS-CoV-2 cellular immunity by whole-blood PCR
- PMID: 35697804
- PMCID: PMC10603792
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01347-6
Rapid, scalable assessment of SARS-CoV-2 cellular immunity by whole-blood PCR
Abstract
Fast, high-throughput methods for measuring the level and duration of protective immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 are needed to anticipate the risk of breakthrough infections. Here we report the development of two quantitative PCR assays for SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell activation. The assays are rapid, internally normalized and probe-based: qTACT requires RNA extraction and dqTACT avoids sample preparation steps. Both assays rely on the quantification of CXCL10 messenger RNA, a chemokine whose expression is strongly correlated with activation of antigen-specific T cells. On restimulation of whole-blood cells with SARS-CoV-2 viral antigens, viral-specific T cells secrete IFN-γ, which stimulates monocytes to produce CXCL10. CXCL10 mRNA can thus serve as a proxy to quantify cellular immunity. Our assays may allow large-scale monitoring of the magnitude and duration of functional T cell immunity to SARS-CoV-2, thus helping to prioritize revaccination strategies in vulnerable populations.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
A.B., A.T. and N.L.B. declare the filling of a patent application relating to the use of peptide pools in whole blood for detection of SARS-CoV-2 T cells (pending). E.G., J.O., M.S., D.T. and D.L.O. declare the filling of a patent application relating to the qTACT and dqTACT assays (pending). S.G. reports consultancy and/or advisory roles for Merck and OncoMed, and research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Genentech, Immune Design, Janssen R&D, Pfizer, Regeneron and Takeda. G.N., I.D.N. and L.C. are employees of Hyris Ltd, manufacturer of the bCUBE machine described in this article. C.L., G.S. and M.F. are employees of Synlab Italy. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

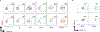


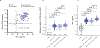






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

