Conditioned taste aversion in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus
- PMID: 35697908
- PMCID: PMC9192700
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13500-x
Conditioned taste aversion in the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus
Abstract
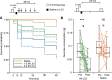
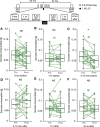
Conditioned taste aversion (CTA) is a form of classical conditioning in which animals associate the taste of a food with illness caused by toxin contained in the food. CTA in mammals is achieved with a long interval of up to several hours between food ingestion and illness induced by LiCl injection. Insects also exhibit CTA, but not much is known about its features. We investigated whether the cricket Gryllus bimaculatus exhibits CTA when ingestion of a sugar solution is followed by LiCl injection. Crickets that ingested sucrose solution 5-10 min before LiCl injection exhibited reduction of sucrose consumption tested 24 or 48 h after injection compared to that tested 24 h before injection. In contrast, crickets that ingested sucrose solution 5-10 min after LiCl injection or 1 h or 8 h before or after injection did not exhibit reduction of sucrose consumption, indicating that reduction of sucrose consumption by CTA training is pairing-specific. We conclude that CTA in crickets is similar to that in mammals in that one-trial pairing is sufficient to achieve memory retention for days, but it differs in that it is achieved with a relatively short interval (< 1 h) between food ingestion and toxin injection.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rapid, labile, and protein synthesis-independent short-term memory in conditioned taste aversion.Learn Mem. 1999 Jan-Feb;6(1):37-46. Learn Mem. 1999. PMID: 10355522 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of AP-1 family transcription factors in the amygdala during conditioned taste aversion learning: role for Fra-2.Brain Res. 2008 May 1;1207:128-41. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.072. Epub 2008 Feb 9. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18374904 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing immune activation (lipopolysaccharide) and toxin (lithium chloride)-induced gustatory conditioning: lipopolysaccharide produces conditioned taste avoidance but not aversion.Behav Brain Res. 2004 Jan 5;148(1-2):11-9. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(03)00181-5. Behav Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14684243
-
Increase of glucocorticoids is not required for the acquisition, but hinders the extinction, of lithium-induced conditioned taste aversion.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 May 5;730:14-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.02.017. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24582760
-
Impairment of the gustatory engram by generalised seizure activity without associated loss of conditioned taste aversion.Physiol Behav. 1993 May;53(5):839-43. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(93)90259-i. Physiol Behav. 1993. PMID: 8390061
References
-
- Garcia J, Ervin FR, Koelling RA. Learning with prolonged delay of reinforcement. Psychonomic Sci. 1966;5:121–122. doi: 10.3758/BF03328311. - DOI
-
- Steinert PA, Infurna RN, Spear NE. Long-term retention of a conditioned taste aversion in preweanling and adult rats. Anim. Learn. Behav. 1980;8:375–381. doi: 10.3758/BF03199620. - DOI
-
- Rosas JM, Bouton ME. Spontaneous recovery after extinction of a conditioned taste aversion. Anim. Learn. Behav. 1996;24:341–348. doi: 10.3758/BF03198982. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

