Synthesis of a 2-nitroimidazole derivative N-(4-[18F]fluorobenzyl)-2-(2-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-acetamide ([18 F]FBNA) as PET radiotracer for imaging tumor hypoxia
- PMID: 35697954
- PMCID: PMC9192864
- DOI: 10.1186/s41181-022-00165-0
Synthesis of a 2-nitroimidazole derivative N-(4-[18F]fluorobenzyl)-2-(2-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-acetamide ([18 F]FBNA) as PET radiotracer for imaging tumor hypoxia
Abstract
Background: Tissue hypoxia is a pathological condition characterized by reducing oxygen supply. Hypoxia is a hallmark of tumor environment and is commonly observed in many solid tumors. Non-invasive imaging techniques like positron emission tomography (PET) are at the forefront of detecting and monitoring tissue hypoxia changes in vivo.
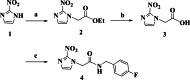
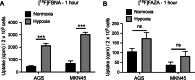
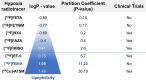
Results: We have developed a novel 18F-labeled radiotracer for hypoxia PET imaging based on cytotoxic agent benznidazole. Radiotracer N-(4-[18F]fluorobenzyl)-2-(2-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetamide ([18F]FBNA) was synthesized through acylation chemistry with readily available 4-[18F]fluorobenzyl amine. Radiotracer [18F]FBNA was obtained in good radiochemical yields (47.4 ± 5.3%) and high radiochemical purity (> 95%). The total synthesis time was 100 min, including HPLC purification and the molar activity was greater than 40 GBq/µmol. Radiotracer [18F]FBNA was stable in saline and mouse serum for 6 h. [18F]FBNA partition coefficient (logP = 1.05) was found to be more lipophilic than [18F]EF-5 (logP = 0.75), [18F]FMISO (logP = 0.4) and [18F]FAZA (logP = - 0.4). In vitro studies showed that [18F]FBNA accumulates in gastric cancer cell lines AGS and MKN45 under hypoxic conditions.
Conclusions: Hence, [18F]FBNA represents a novel and easy-to-prepare PET radioligand for imaging hypoxia.
Keywords: Hypoxia; N-(4-[18F]fluorobenzyl)-2-(2-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetamide ([18F]FBNA); Positron emission tomography (PET).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
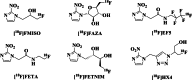
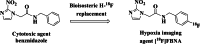


Similar articles
-
Comparison of three 18F-labeled 2-nitroimidazoles for imaging hypoxia in breast cancer xenografts: [18F]FBNA, [18F]FAZA and [18F]FMISO.Nucl Med Biol. 2023 Sep-Oct;124-125:108383. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2023.108383. Epub 2023 Aug 26. Nucl Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37651917
-
2-(2-Nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)-N-(2,2,3,3,3-[18F]pentafluoropropyl)-acetamide.2005 Nov 8 [updated 2005 Dec 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2005 Nov 8 [updated 2005 Dec 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20641211 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
2-[18F]Fluoro-N-(2-(2-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)ethyl)acetamide.2011 Jul 19 [updated 2011 Oct 13]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Jul 19 [updated 2011 Oct 13]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 22013607 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
[18F]-3-Fluoro-2-(4-((2-nitro-1H-imidazol-1-yl)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl)propan-1-ol.2010 Aug 16 [updated 2010 Sep 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2010 Aug 16 [updated 2010 Sep 23]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 20945565 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Synthesis and evaluation of two novel 2-nitroimidazole derivatives as potential PET radioligands for tumor imaging.Nucl Med Biol. 2011 May;38(4):501-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2010.11.001. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Nucl Med Biol. 2011. PMID: 21531287 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Highlight selection of radiochemistry and radiopharmacy developments by editorial board.EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2022 Oct 1;7(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s41181-022-00177-w. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem. 2022. PMID: 36182995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging hypoxia for head and neck cancer: current status, challenges, and prospects.Theranostics. 2025 Jul 11;15(16):8012-8030. doi: 10.7150/thno.112781. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 40860130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pattern of GH Action in the Mouse Brain.Endocrinology. 2024 May 27;165(7):bqae057. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae057. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38728240 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in PET and SPECT Radiotracers as Radiopharmaceuticals for Hypoxia Tumors.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 27;15(7):1840. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071840. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514026 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Askoxylakis V, Dinkel J, Eichinger M, Stieltjes B, Sommer G, Strauss LG, Dimitrakopoulou SA, Schneider AK, Haberkorn U, Huber PEL, Bischof M, Debus J, Thieke C. Multimodal hypoxia imaging and intensity modulated radiation therapy for unresectable non-small-cell lung cancer: the HIL trial. Radiat Oncol. 2012;7:157. doi: 10.1186/1748-717X-7-157. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bern C, Montgomery SP, Herwaldt BL, Anis R, Dantas RO, Maguire JH, Acquatella H, Morillo C, Kirchhoff LV, Gilman RH, Reyes PA, Salvatella R, Moore AC. Evaluation and treatment of chagas disease in the United States: a systematic review. JAMA. 2007;298:2171–2181. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.18.2171. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
