Efficacy of celery (Apium graveolens L.) alcoholic extract against systemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in rat models
- PMID: 35698524
- PMCID: PMC9178570
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.898-905
Efficacy of celery (Apium graveolens L.) alcoholic extract against systemic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection in rat models
Abstract
Background and aim: The coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) pandemic caused global economic and health problems. The pandemic increased the number of infectious diseases categorized as neglected diseases, such as staphylococcosis, which is caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Celery is an herb that consist of antioxidants that can potentially act as antimicrobial agents. This study aimed to analyze the efficacy of celery alcoholic extract against systemic MRSA infections in rat models.
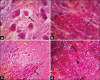
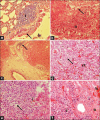
Materials and methods: In this study, 36 male, 6-month-old Sprague-Dawley rats (average weight: 300 g) were used as models. The rats were divided into six groups: Group K- (negative control), Group K+ (infected with MRSA without therapy), Group V (infected with MRSA+100 mg vancomycin per kg body weight [BW]), Group P1 (infected with MRSA+1 mg celery extract per kg BW), Group P2 (infected with MRSA+2 mg celery extract per kg BW), and Group P4 (infected with MRSA+4 mg celery extract per kg BW). The therapy was given once daily for 7 days. Blood and organs were taken on day 7 for hematology, serology, immunohistochemistry, and histopathology.
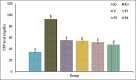
Results: Results showed that 4 mg celery extract per kg BW promotes the healing of MRSA systemic infections in rat models (p≤0.05). The better prognosis was indicated by the normalization of red blood cell indices, white blood cell, neutrophil and lymphocyte counts, Cluster of differentiation 4+, Cluster of differentiation 8+, and Cyclooxygenase-2 expression and absence of severe tissue damage. Celery extracts inhibited MRSA growth in the blood samples.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that celery alcoholic extract can potentially be used as an antimicrobial agent against systemic MRSA infections. A clinical study regarding the efficacy of celery extract must be conducted to ensure its potency against MRSA infections in humans.
Keywords: celery; efficacy; healing; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus; systemic infection.
Copyright: © Prakoso and Wijayanti, et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Celery (Apium graveolens) as a potential antibacterial agent and its effect on cytokeratin-17 and other healing promoters in skin wounds infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Vet World. 2020 May;13(5):865-871. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.865-871. Epub 2020 May 9. Vet World. 2020. PMID: 32636580 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Apium graveolens Extract Administration on the Pharmacokinetics of Captopril in the Plasma of Rats.Sci Pharm. 2018 Feb 16;86(1):6. doi: 10.3390/scipharm86010006. Sci Pharm. 2018. PMID: 29462958 Free PMC article.
-
[A multicentric study on clinical characteristics and antibiotic sensitivity in children with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Aug 2;58(8):628-634. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20200505-00469. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32842382 Chinese.
-
Potential antimicrobial properties of the Ulva lactuca extract against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus-infected wounds: A review.Vet World. 2021 May;14(5):1116-1123. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2021.1116-1123. Epub 2021 May 8. Vet World. 2021. PMID: 34220111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of the Antioxidant Activity of Celery ( Apium graveolens L).J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2017 Oct;22(4):1029-1034. doi: 10.1177/2156587217717415. Epub 2017 Jul 13. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28701046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garoy E.Y, Gebreab Y.B, Achila O.O, Tekeste D.G, Kesete R, Ghirmay R, Kiflay R, Tesfu T. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA):Prevalence and antimicrobial sensitivity pattern among patients-a multicenter study in Asmara, Eritrea. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2019;2019:8321834. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
