Human Health Risk Assessment of 4-12 GHz Radar Waves using CST STUDIO SUITE Software
- PMID: 35698536
- PMCID: PMC9175128
- DOI: 10.31661/jbpe.v0i0.1272
Human Health Risk Assessment of 4-12 GHz Radar Waves using CST STUDIO SUITE Software
Abstract
Background: The application of radar systems in telecommunications and aerospace science is important. However, engineering department's staff various tissues are always under chronic radiation generated by the radar fields which may affect health.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the risk of radar wave exposure and to explore the effects and limitations.
Material and methods: In this simulation study, an adult body model versus 1 watt source with a distance of 50 centimeters exposure has been simulated using the CST STUDIO SUITE. Furthermore, various physical and electrical properties of each tissue and organ for different frequencies and exposure times have been studied. The exposure dose limitations have been considered using the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) safety and health guide report.
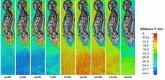
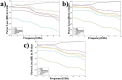
Results: Total body absorbed doses for 4 GHz, 8 GHz, and 12 GHz frequency, and 6 min, 4 h, and 30 days exposure time, have been calculated as 1.136×10-5, 1.598×10-5, 1.58×10-3, 1.521×10-5, 3.122×10-5, 4.52×10-3, 4.1×10-5, 10-4, and 10-2, respectively.
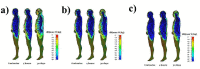
Conclusion: It has shown that the internal organs of the body and head will be under more risk by reducing radar frequencies from 12 GHz to 4 GHz. On the other hand, the higher frequency can cause a higher risk to the human skin. In addition, the maximum Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) for each case has been calculated. The results show that for this normalized source, the safety criteria have been respected, but for a higher source, the calculations must be repeated.
Keywords: CST Studio; Human Health; Risk Assessment; SAR; Synapses; Ventricular.
Copyright: © Journal of Biomedical Physics and Engineering.
Figures

References
-
- Madhukar A, Park Y, Kim W, Sunaryanto HJ, Berlin R, Chamorro LP, Bentsman J, Ostoja-Starzewski M. Heat conduction in porcine muscle and blood: experiments and time-fractional telegraph equation model. Journal of the Royal Society Interface . 2019;16(160):20190726. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2019.0726. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Foster K, Colombi D. Thermal response of tissue to RF exposure from canonical dipoles at frequencies for future mobile communication systems. Electron Letters . 2017;53(5):360–2. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.3488. - DOI
-
- Gabriel C, Peyman A. Chapter 69 - Dielectric Properties of Biological Tissues; Variation with Age. Jeffrey L. Ram, P, Editors. Michael Conn, Conn’s Handbook of Models for Human Aging. 2nd Edition. Elsevier; 2018. p. 939-52
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
