Median Effective Concentration of Ropivacaine for Femoral Nerve Block Maintaining Motor Function During Knee Arthroscopy in Two Age Groups
- PMID: 35698568
- PMCID: PMC9188396
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S357750
Median Effective Concentration of Ropivacaine for Femoral Nerve Block Maintaining Motor Function During Knee Arthroscopy in Two Age Groups
Abstract
Background: Femoral nerve block combined with general anesthesia is commonly used for patients undergoing knee arthroscopy in ambulatory care centers. An ideal analgesic agent would selectively (differentially) block sensory fibers, with little or no effect on motor nerves. Ropivacaine is considered to cause less motor block than others. This study investigated the median effective concentration (EC50) of ropivacaine for differential femoral nerve block in adults either younger or older than 60 years.
Methods: Patients with American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status I-III and scheduled for knee arthroscopy were categorized as 18- to 60-years-old (Group 1), or older than 60 years (Group 2). Surgeries were performed under general anesthesia combined with femoral nerve block via 22 mL ropivacaine. The EC50 of ropivacaine for differential femoral nerve block was determined using the up-and-down method and probit regression. The primary outcome was the EC50 (95% confidence interval [CI]) of the 2 groups. Data on the sensory block, analgesic effect, complications, and hemodynamics during surgery were also recorded.
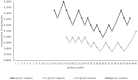
Results: The EC50 of 22 mL ropivacaine for differential femoral nerve block of Group 1 (0.124%, 95% CI 0.097-0.143%) was significantly higher than that of Group 2 (0.088%, 95% CI 0.076-0.103%). The sensory block and hemodynamic data of the 2 groups were comparable. None of the patients experienced neurological complications.
Conclusion: The EC50 of ropivacaine administered for differential femoral nerve block during knee arthroscopy was lower in patients older than 60 years, relative to younger adults.
Keywords: EC50; age groups; femoral nerve block; motor block; ropivacaine.
© 2022 Tai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Yang X, Kang W, Xiong W, et al. The effect of dexmedetomidine as adjuvant to ropivacaine 0.1% for femoral nerve block on strength of quadriceps muscle in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. J Pain Res. 2019;12:3355–3363. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S217283 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

