Research Progress of Liujunzi Decoction in the Treatment of Tumor-Associated Anorexia
- PMID: 35698654
- PMCID: PMC9188393
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S365292
Research Progress of Liujunzi Decoction in the Treatment of Tumor-Associated Anorexia
Abstract
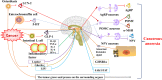
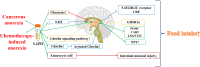
Tumor-associated anorexia, mainly including cancerous anorexia and chemotherapy-induced anorexia, severely reduces the life quality of cancer patients but lacks of effective control until now. Liujunzi decoction (LJZD), a classical tonifying formula in traditional Chinese medicine, has promising effect in preventing and treating many kinds of anorexia. A growing number of evidence showed that LJZD is able to improve tumor-associated anorexia. Up to March 2022, a total of 58 articles studying LJZD or Rikkunshito (the name of LJZD in Japanese herbal medicine) in the treatment of tumor-associated anorexia are searched out in PubMed. This paper summarizes the effect of LJZD in ameliorating tumor-associated anorexia, in order to provide a theoretical basis for the clinical application of LJZD in treating tumor-associated anorexia, laying foundation for further research.
Keywords: Liujunzi decoction; review; tumor-associated anorexia.
© 2022 Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liujunzi Decoction ameliorated cisplatin-induced anorexia by inhibiting the JAK-STAT signaling pathway and coordinating anorexigenic and orexigenic neuropeptides in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;285:114840. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114840. Epub 2021 Nov 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34800646
-
Liujunzi decoction exerts potent antitumor activity in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma by inhibiting miR-34a/STAT3/IL-6R feedback loop, and modifies antitumor immunity.Phytomedicine. 2023 Mar;111:154672. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154672. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36701994
-
The Therapeutic Effect of Traditional LiuJunZi Decoction on Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma in Balb/C Mice.Can Respir J. 2021 Sep 29;2021:6406295. doi: 10.1155/2021/6406295. eCollection 2021. Can Respir J. 2021. PMID: 34630778 Free PMC article.
-
[Systematic review and Meta-analysis on efficacy and safety of Liujunzi Decoction combined with Western medicine for stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Nov;45(22):5331-5343. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200720.501. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33350192 Chinese.
-
Cancer cachexia pathophysiology and translational aspect of herbal medicine.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013 Jul;43(7):695-705. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyt075. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23737606 Review.
Cited by
-
Traditional Chinese medicine in lung cancer treatment.Mol Cancer. 2025 Feb 26;24(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02245-6. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40001110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Benefits of In Silico Methods: A Promising Alternative in Natural Compound's Drug Discovery and Repurposing for HBV Therapy.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Mar 16;18(3):419. doi: 10.3390/ph18030419. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40143195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Mechanism of Liujunzi Decoction in the Treatment of Breast Cancer based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(9):702-726. doi: 10.2174/0113816128289900240219104854. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 38415453
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical