High rate of tibial debonding and failure in a popular knee replacement : a follow-up review
- PMID: 35698801
- PMCID: PMC9233423
- DOI: 10.1302/2633-1462.36.BJO-2022-0043.R1
High rate of tibial debonding and failure in a popular knee replacement : a follow-up review
Abstract
Aims: Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is a common and safe orthopaedic procedure. Zimmer Biomet's NexGen is the second most popular brand of implant used in the UK. The primary cause of revision after the first year is aseptic loosening. We present our experience of using this implant, with significant concerns around its performance with regards early aseptic loosening of the tibial component.
Methods: A retrospective, single-surgeon review was carried out of all of the NexGen Legacy Posterior Stabilized (LPS) TKAs performed in this institute. The specific model used for the index procedures was the NexGen Complete Knee System (Legacy Knee-Posterior Stabilized LPS-Flex Articular Surface, LPS-Flex Femoral Component Option, and Stemmed Nonaugmentable Tibial Component Option).
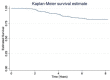
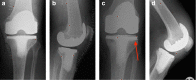
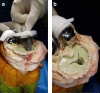
Results: Between 2013 and 2016, 352 NexGen TKAs were carried out on 331 patients. A total of 62 TKAs have been revised to date, giving an all-cause revision rate of 17.6% at a minimum of five years. Three of these revisions were due to infection. Overall, 59 of the revisions were performed for aseptic loosening (16.7%) of the tibial component. The tibial component was removed intraoperatively without instrumentation due to significant tibial debonding between the implant-cement interface.
Conclusion: While overall, we believe that early aseptic loosening is multi-factorial in nature, the significantly high aseptic revision rate, as seen by an experienced fellowship-trained arthroplasty surgeon, has led us to believe that there is a fundamental issue with this NexGen implant design. Continued implant surveillance and rigorous review across all regions using this particular implant is warranted based on the concerning findings described here. Cite this article: Bone Jt Open 2022;3(6):495-501.
Keywords: Aseptic Loosening; Early Implant Failure; Femoral Component; Infection; NexGen; Tibial Tray Failure; Total Knee Arthroplasty; Zimmer; arthroplasty surgeon; aseptic loosening; knee arthroplasties; knees; orthopaedic procedure; single-surgeon; tibial components; total knee arthroplasty (TKA).
Figures
References
-
- No authors listed . NJR 17th Annual Report 2020. https://reports.njrcentre.org.uk/Portals/0/PDFdownloads/NJR%2017th%20Ann... (date last accessed 1 June 2022).
-
- Patel A, Pavlou G, Mújica-Mota RE, Toms AD. The epidemiology of revision total knee and hip arthroplasty in England and Wales: A comparative analysis with projections for the United States. A study using the National Joint Registry dataset. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(8):1076–1081. 10.1302/0301-620X.97B8.35170 - DOI - PubMed

