Hepatotoxic mechanism of diclofenac sodium on broiler chicken revealed by iTRAQ-based proteomics analysis
- PMID: 35698810
- PMCID: PMC9346521
- DOI: 10.4142/jvs.22018
Hepatotoxic mechanism of diclofenac sodium on broiler chicken revealed by iTRAQ-based proteomics analysis
Abstract
Background: At the therapeutic doses, diclofenac sodium (DFS) has few toxic side effects on mammals. On the other hand, DFS exhibits potent toxicity against birds and the mechanisms remain ambiguous.
Objectives: This paper was designed to probe the toxicity of DFS exposure on the hepatic proteome of broiler chickens.
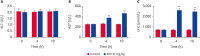
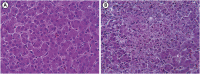
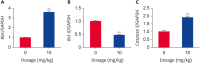
Methods: Twenty 30-day-old broiler chickens were randomized evenly into two groups (n = 10). DFS was administered orally at 10 mg/kg body weight in group A, while the chickens in group B were perfused with saline as a control. Histopathological observations, serum biochemical examinations, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction were performed to assess the liver injury induced by DFS. Proteomics analysis of the liver samples was conducted using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification (iTRAQ) technology.
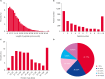
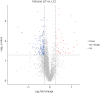
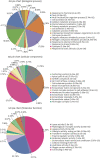
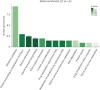
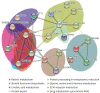
Results: Ultimately, 201 differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) were obtained, of which 47 were up regulated, and 154 were down regulated. The Gene Ontology classification and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis were conducted to screen target DEPs associated with DFS hepatotoxicity. The regulatory relationships between DEPs and signaling pathways were embodied via a protein-protein interaction network. The results showed that the DEPs enriched in multiple pathways, which might be related to the hepatotoxicity of DFS, were "protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum," "retinol metabolism," and "glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism."
Conclusions: The hepatotoxicity of DFS on broiler chickens might be achieved by inducing the apoptosis of hepatocytes and affecting the metabolism of retinol and purine. The present study could provide molecular insights into the hepatotoxicity of DFS on broiler chickens.
Keywords: Diclofenac sodium; chicken; liver; proteomics; toxicity.
© 2022 The Korean Society of Veterinary Science.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis reveals the toxic mechanism of diclofenac sodium on the kidney of broiler chicken.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021 Nov;249:109129. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.109129. Epub 2021 Jul 3. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34229076
-
iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analyses the cycle chronic heat stress affecting liver proteome in yellow-feather chickens.Poult Sci. 2021 Jun;100(6):101111. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101111. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Poult Sci. 2021. PMID: 33965807 Free PMC article.
-
iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis reveals key proteins affecting cardiac function in broilers that died of sudden death syndrome.Poult Sci. 2019 Dec 1;98(12):6472-6482. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez532. Poult Sci. 2019. PMID: 31509194 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary Se deficiency dysregulates metabolic and cell death signaling in aggravating the AFB1 hepatotoxicity of chicks.Food Chem Toxicol. 2021 Mar;149:111938. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2020.111938. Epub 2020 Dec 24. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33348051
-
Proteomic analysis using isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantification technology reveals mechanisms of toxic effects of tris (1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) phosphate on RAW264.7 macrophage cells.J Appl Toxicol. 2022 Feb;42(2):190-202. doi: 10.1002/jat.4201. Epub 2021 May 25. J Appl Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34036598
Cited by
-
Phosphoproteomics Profile of Chicken Cecum in the Response to Salmonella enterica Serovar Enteritidis Inoculation.Animals (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;13(1):78. doi: 10.3390/ani13010078. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36611688 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Mechanism of Luteolin in Protecting Chickens from Ammonia Poisoning Based on Proteomic Technology.Metabolites. 2025 May 14;15(5):326. doi: 10.3390/metabo15050326. Metabolites. 2025. PMID: 40422902 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of myeloid-related protein 126, cardiac troponin C and serum amyloid A as potential plasma biomarkers of health and disease in sea turtles.Conserv Physiol. 2025 Aug 14;13(1):coaf061. doi: 10.1093/conphys/coaf061. eCollection 2025. Conserv Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40823445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ertekin T, Bilir A, Aslan E, Koca B, Turamanlar O, Ertekin A, et al. The effect of diclofenac sodium on neural tube development in the early stage of chick embryos. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 2019;78(2):307–313. - PubMed
-
- Bertocchi P, Antoniella E, Valvo L, Alimonti S, Memoli A. Diclofenac sodium multisource prolonged release tablets--a comparative study on the dissolution profiles. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2005;37(4):679–685. - PubMed
-
- Gan TJ. Diclofenac: an update on its mechanism of action and safety profile. Curr Med Res Opin. 2010;26(7):1715–1731. - PubMed
-
- Sharma S, Setia H, Toor AP. Assessing the bioremediation potential of indigenously isolated Klebsiella sp. WAH1 for diclofenac sodium: optimization, toxicity and metabolic pathway studies. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021;37(2):33. - PubMed
-
- Menassé R, Hedwall PR, Kraetz J, Pericin C, Riesterer L, Sallmann A, et al. Pharmacological properties of diclofenac sodium and its metabolites. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1978;7(22):5–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021TSGC1271/Innovation Ability Promotion Project for Technology-based Small and Medium Enterprise in Shandong Province/China
- 2021TSGC1275/Innovation Ability Promotion Project for Technology-based Small and Medium Enterprise in Shandong Province/China
- YDZX20203700003775/Shandong Provincial Central Government Guides Local Technology Development Fund Projects/China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

