The role of suprascapular nerve block in hydrodilatation for frozen shoulder
- PMID: 35699461
- PMCID: PMC9196022
- DOI: 10.1051/sicotj/2022026
The role of suprascapular nerve block in hydrodilatation for frozen shoulder
Abstract
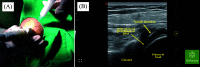
Introduction: Frozen shoulder is a debilitating problem that requires comprehensive diagnosis and management. Patients usually recover, but the possibility of not reobtaining a full range of motion exists. Thus, early shoulder exercises are necessary to achieve their full range of motion. This study aims to understand the effects of suprascapular nerve block (SSNB) augmentation at the spinoglenoid notch in hydrodilatation to treat frozen shoulder to facilitate early shoulder exercises.
Methods: The current study retrospectively observed 31 patients, including 40-60-year-old patients diagnosed and treated with primary frozen shoulder. The participants were divided into groups A (hydrodilatation) and B (hydrodilatation and the augmentation of an SSNB). Shoulder function and pain scores were assessed before, during, and after the intervention (at months 1 and 6).
Results: The result of this study shows that suprascapular nerve block plays a role in decreasing pain in intraintervention (0.69 vs. 5.73; p < 0.05), month 1 of follow-up (3.44 vs. 6.40; p < 0.05), but not significant on month 6 of group A and B after intervention (5.88 vs. 7.20; p > 0.05). Better delta functional scores were noted in the therapy group during month 1 of the follow-up (delta American shoulder and elbow surgeons [ASES]: 19.29 vs. 34.40, p < 0.05; delta disabilities of the arm, shoulder, and hand [DASH]: 17.88 vs. 38.15, p < 0.05). The difference in functional score on month 6 between both groups was not significantly different (delta ASES: 31.97 vs. 30.31, p > 0.05; delta DASH: 36.63 vs. 38.92, p > 0.05).
Discussion: One rationale for using an SSNB augmentation at spinoglenoid notch in hydrodilatation for treating frozen shoulder was to obtain pain relief immediately to facilitate early manual exercise. SSNB has positive effects on short-term evaluation of shoulder pain and function after glenohumeral hydrodilatation, but not in the long term.
Keywords: Corticosteroid; Frozen shoulder; Hydrodilatation; Spinoglenoid notch; Suprascapular nerve block.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2022.
Figures

References
-
- Sonune S, Gaur A, Gupta S (2016) Comparative study of ultrasound guided supra-scapular nerve block versus intra-articular steroid injection in frozen shoulder. Int J Res Orthop 2, 387.
-
- Lubis AM, Lubis VK (2013) Matrix metalloproteinase, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase and transforming growth factor-beta 1 in frozen shoulder, and their changes as response to intensive stretching and supervised neglect exercise. J Orthop Sci: Offl J Jpn Orthop Assoc 18(4), 519. - PubMed
-
- Eljabu W, Klinger HM, von Knoch M (2016) Prognostic factors and therapeutic options for treatment of frozen shoulder: A systematic review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 136(1), 1. - PubMed
-
- Lädermann A, Piotton S, Abrassart S, Mazzolari A, Ibrahim M, Stirling P (2021) Hydrodilatation with corticosteroids is the most effective conservative management for frozen shoulder. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 29(8), 2553. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
