Site-specific glycosylation of SARS-CoV-2: Big challenges in mass spectrometry analysis
- PMID: 35700310
- PMCID: PMC9349404
- DOI: 10.1002/pmic.202100322
Site-specific glycosylation of SARS-CoV-2: Big challenges in mass spectrometry analysis
Abstract
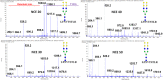
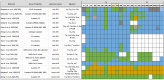
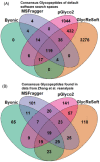
Glycosylation of viral proteins is required for the progeny formation and infectivity of virtually all viruses. It is increasingly clear that distinct glycans also play pivotal roles in the virus's ability to shield and evade the host's immune system. Recently, there has been a great advancement in structural identification and quantitation of viral glycosylation, especially spike proteins. Given the ongoing pandemic and the high demand for structure analysis of SARS-CoV-2 densely glycosylated spike protein, mass spectrometry methodologies have been employed to accurately determine glycosylation patterns. There are still many challenges in the determination of site-specific glycosylation of SARS-CoV-2 viral spike protein. This is compounded by some conflicting results regarding glycan site occupancy and glycan structural characterization. These are probably due to differences in the expression systems, form of expressed spike glycoprotein, MS methodologies, and analysis software. In this review, we recap the glycosylation of spike protein and compare among various studies. Also, we describe the most recent advancements in glycosylation analysis in greater detail and we explain some misinterpretation of previously observed data in recent publications. Our study provides a comprehensive view of the spike protein glycosylation and highlights the importance of consistent glycosylation determination.
Keywords: N-glycosylation; O-glycosylation; SARS-CoV-2 glycoprotein; glycoproteomics.
© 2022 The Authors. Proteomics published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
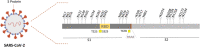


References
-
- Braun, L. , Brenier‐Pinchart, M.‐P. , Yogavel, M. , Curt‐Varesano, A. , Curt‐Bertini, R.‐L. , Hussain, T. , Kieffer‐Jaquinod, S. , Coute, Y. , Pelloux, H. , Tardieux, I. , Sharma, A. , Belrhali, H. , Bougdour, A. , & Hakimi, M.‐A. (2013). A Toxoplasma dense granule protein, GRA24, modulates the early immune response to infection by promoting a direct and sustained host p38 MAPK activation. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 210(10), 2071–2086. 10.1084/jem.20130103 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duyen, H. T. L. , Ngoc, T. V. , Ha, D. T. , Hang, V. T. T. , Kieu, N. T. T. , Young, P. R. , Farrar, J. J. , Simmons, C. P. , Wolbers, M. , & Wills, B. A. (2011). Kinetics of plasma viremia and soluble nonstructural protein 1 concentrations in dengue: Differential effects according to serotype and immune status. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 203(9), 1292–1300. 10.1093/infdis/jir014 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

