The role of sense of community in improving the health-related quality of life among Black Americans
- PMID: 35700438
- PMCID: PMC9742166
- DOI: 10.1002/jcop.22901
The role of sense of community in improving the health-related quality of life among Black Americans
Abstract
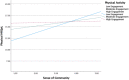
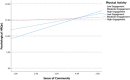
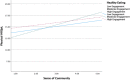
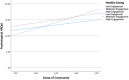
Black Americans have the lowest life expectancy and health-related quality of life (HRQoL; a strong predictor of premature mortality) of any racial/ethnic group in the United States. Low rates of physical activity and engagement in healthy eating are two known contributors to low HRQoL. Black Americans are more likely to live in environments that inhibit engagement in these two contributors. The present study examined sense of community as a buffer against the adverse effects of low physical activity and healthy eating on HRQoL among Black Americans. A sample of 290 Black American adults were recruited for the present study. Results indicate that sense of community buffers against the adverse effects of low physical activity on HRQoL. The results of the present study can be used by health promotion interventionists and policy-makers to improve HRQoL and reduce premature mortality among Black Americans.
Keywords: Black Americans; health promotion; health-related quality of life; sense of community.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Community Psychology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arias, E. , Tejada‐Vera, B. , & Ahmad, F. (2021). Provisional lifes expectancy estimates for January through June, 2020. US Department of Health and Human Services. Retrieved October 29, 2021 from https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/vsrr/VSRR10-508.pdf
-
- Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: experiments by nature and design. Harvard University Press.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

