MiR-690 treatment causes decreased fibrosis and steatosis and restores specific Kupffer cell functions in NASH
- PMID: 35700738
- PMCID: PMC9262870
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2022.05.008
MiR-690 treatment causes decreased fibrosis and steatosis and restores specific Kupffer cell functions in NASH
Abstract
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a liver disease associated with significant morbidity. Kupffer cells (KCs) produce endogenous miR-690 and, via exosome secretion, shuttle this miRNA to other liver cells, such as hepatocytes, recruited hepatic macrophages (RHMs), and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). miR-690 directly inhibits fibrogenesis in HSCs, inflammation in RHMs, and de novo lipogenesis in hepatocytes. When an miR-690 mimic is administered to NASH mice in vivo, all the features of the NASH phenotype are robustly inhibited. During the development of NASH, KCs become miR-690 deficient, and miR-690 levels are markedly lower in mouse and human NASH livers than in controls. KC-specific KO of miR-690 promotes NASH pathogenesis. A primary target of miR-690 is NADK mRNA, and NADK levels are inversely proportional to the cellular miR-690 content. These studies show that KCs play a central role in the etiology of NASH and raise the possibility that miR-690 could emerge as a therapeutic for this condition.
Keywords: Kupffer cell; NASH; fibrosis; inflammation; liver; miR-690; steatosis.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests W.Y. and J.M.O. are co-investigators on a provisional patent covering the use of miR-690 as an insulin sensitizer.
Figures

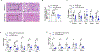
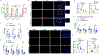
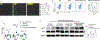
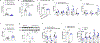

Comment in
-
Targeting De Novo Lipogenesis by Different Approaches Shows Promise in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Gastroenterology. 2022 Nov;163(5):1472. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.07.085. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Gastroenterology. 2022. PMID: 35963367 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anstee QM, Targher G, and Day C (2013). Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology 10, 330–344. - PubMed
-
- Bonnardel J, T’Jonck W, Gaublomme D, Browaeys R, Scott CL, Martens L, Vanneste B, De Prijck S, Nedospasov SA, Kremer A, et al. (2019). Stellate Cells, Hepatocytes, and Endothelial Cells Imprint the Kupffer Cell Identity on Monocytes Colonizing the Liver Macrophage Niche. Immunity 51, 638–654.e639. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Broutier L, Andersson-Rolf A, Hindley CJ, Boj SF, Clevers H, Koo B-K, and Huch M (2016). Culture and establishment of self-renewing human and mouse adult liver and pancreas 3D organoids and their genetic manipulation. Nature Protocols 11, 1724–1743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R00 DK115998/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK125560/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK120515/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA029019/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK009920/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA028550/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA022614/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA018663/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK111866/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099205/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R44 DK115242/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101395/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

