Global O-GlcNAcylation changes impact desmin phosphorylation and its partition toward cytoskeleton in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells differentiated into myotubes
- PMID: 35701470
- PMCID: PMC9198038
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-14033-z
Global O-GlcNAcylation changes impact desmin phosphorylation and its partition toward cytoskeleton in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells differentiated into myotubes
Abstract
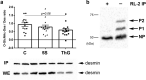
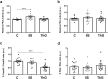
Desmin is the guardian of striated muscle integrity, permitting the maintenance of muscle shape and the efficiency of contractile activity. It is also a key mediator of cell homeostasis and survival. To ensure the fine regulation of skeletal muscle processes, desmin is regulated by post-translational modifications (PTMs). It is more precisely phosphorylated by several kinases connecting desmin to intracellular processes. Desmin is also modified by O-GlcNAcylation, an atypical glycosylation. However, the functional consequence of O-GlcNAcylation on desmin is still unknown, nor its impact on desmin phosphorylation. In a model of C2C12 myotubes, we modulated the global O-GlcNAcylation level, and we determined whether the expression, the PTMs and the partition of desmin toward insoluble material or cytoskeleton were impacted or not. We have demonstrated in the herein paper that O-GlcNAcylation variations led to changes in desmin behaviour. In particular, our data clearly showed that O-GlcNAcylation increase led to a decrease of phosphorylation level on desmin that seems to involve CamKII correlated to a decrease of its partition toward cytoskeleton. Our data showed that phosphorylation/O-GlcNAcylation interplay is highly complex on desmin, supporting that a PTMs signature could occur on desmin to finely regulate its partition (i.e. distribution) with a spatio-temporal regulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Impact of MG132 induced-proteotoxic stress on αB-crystallin and desmin phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation and their partition towards cytoskeleton.Biochimie. 2024 Nov;226:121-135. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2024.04.004. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Biochimie. 2024. PMID: 38636798
-
O-GlcNAcylation is a key modulator of skeletal muscle sarcomeric morphometry associated to modulation of protein-protein interactions.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Sep;1860(9):2017-30. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.06.011. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27301331
-
A novel 2D-electrophoresis method for the simultaneous visualization of phosphorylated and O-GlcNAcylated proteoforms of a protein.Electrophoresis. 2024 Sep;45(17-18):1618-1629. doi: 10.1002/elps.202400043. Epub 2024 May 3. Electrophoresis. 2024. PMID: 38700120
-
Desmin and its molecular chaperone, the αB-crystallin: How post-translational modifications modulate their functions in heart and skeletal muscles?Biochimie. 2024 Jan;216:137-159. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2023.10.002. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Biochimie. 2024. PMID: 37827485 Review.
-
O-GlcNAcylation as a regulator of the functional and structural properties of the sarcomere in skeletal muscle: An update review.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020 Jan;228(1):e13301. doi: 10.1111/apha.13301. Epub 2019 Jun 12. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020. PMID: 31108020 Review.
Cited by
-
A Deficiency in Glutamine-Fructose-6-Phosphate Transaminase 1 (Gfpt1) in Skeletal Muscle Results in Reduced Glycosylation of the Delta Subunit of the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (AChRδ).Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 3;14(10):1252. doi: 10.3390/biom14101252. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39456185 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic sequencing and differential analysis of Kazakh horse muscles from various anatomical locations.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Jul 24;12:1633786. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1633786. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40777832 Free PMC article.
-
Posttranslational Modifications of α-Synuclein, Their Therapeutic Potential, and Crosstalk in Health and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Pharmacol Rev. 2024 Oct 16;76(6):1254-1290. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.123.001111. Pharmacol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39164116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute resistance exercise and training reduce desmin phosphorylation at serine 31 in human skeletal muscle, making the protein less prone to cleavage.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 14;14(1):28079. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79385-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39543356 Free PMC article.
-
TANGO2 binds crystallin alpha B and its loss causes desminopathy.Nat Commun. 2025 Jun 6;16(1):5261. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60563-1. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40480980 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

