Far infrared light irradiation enhances Aβ clearance via increased exocytotic microglial ATP and ameliorates cognitive deficit in Alzheimer's disease-like mice
- PMID: 35701825
- PMCID: PMC9195249
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-022-02521-y
Far infrared light irradiation enhances Aβ clearance via increased exocytotic microglial ATP and ameliorates cognitive deficit in Alzheimer's disease-like mice
Abstract
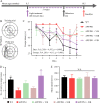
Background: Exposure to sunlight may decrease the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease (AD), and visible and near infrared light have been proposed as a possible therapeutic strategy for AD. Here, we investigated the effects of the visible, near infrared and far infrared (FIR) light on the cognitive ability of AD mice, and found that FIR light also showed potential in the improvement of cognitive dysfunction in AD. However, the related mechanism remains to be elucidated.
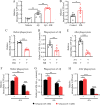
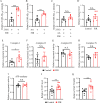
Methods: Morris water maze was used to evaluate the cognitive ability of APPswe/PSEN1dE9 double-transgenic AD mice after light treatment. Western blot was carried out to detect the expression of protein involved in synaptic function and amyloid-β (Aβ) production. The protein amount of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, Aβ1-40 and Aβ1-42 were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The mRNA level of receptors was performed using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Immunostaining was performed to characterize the Aβ burden and microglial Aβ phagocytosis in the brain of AD mice. The Aβ phagocytosis of primary cultured microglia and BV2 were assessed by flow cytometry. The energy metabolism changes were evaluated using related assay kits, including adenosine triphosphate (ATP), lactate content, mitochondrial respiratory chain complex enzymatic activity and oxidized/reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide assay kits.
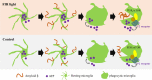
Results: Our results showed that FIR light reduced Aβ burden, a hallmark of AD neuropathology, alleviated neuroinflammation, restored the expression of the presynaptic protein synaptophysin, and ameliorated learning and memory impairment in the AD mice. FIR light enhanced mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation pathway to increase ATP production. This increased intracellular ATP promoted the extracellular ATP release from microglia stimulated by Aβ, leading to the enhanced Aβ phagocytosis through phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin pathways for Aβ clearance.
Conclusions: Our findings have uncovered a previously unappreciated function of FIR light in inducing microglial phagocytosis to clean Aβ, which may be the mechanisms for FIR light to improve cognitive dysfunction in AD mice. These results suggest that FIR light treatment is a potential therapeutic strategy for AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid-β clearance; Energy mechanism; Far infrared light; Microglial phagocytosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Far-Infrared Radiation Ameliorates the Cognitive Dysfunction in an Alzheimer's Disease Transgenic Mouse via Modulating Jak-2/Stat3 and Nrf-2/HO-1 Pathways.Neuromolecular Med. 2025 May 15;27(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s12017-025-08860-2. Neuromolecular Med. 2025. PMID: 40374872 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitating microglial phagocytosis by which Jiawei Xionggui Decoction alleviates cognitive impairment via TREM2-mediated energy metabolic reprogramming.Chin J Nat Med. 2025 Aug;23(8):909-919. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(25)60927-7. Chin J Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 40754372
-
Ouabain Ameliorates Alzheimer's Disease-Associated Neuropathology and Cognitive Impairment in FAD4T Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 20;16(20):3558. doi: 10.3390/nu16203558. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39458551 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of CX3CR1 and Fractalkine Chemokines in Amyloid Beta Clearance and p-Tau Accumulation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) Rodent Models: Is Fractalkine a Systemic Biomarker for AD?Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(4):403-12. doi: 10.2174/1567205013666151116125714. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016. PMID: 26567742 Review.
-
Microglia and microglial-based receptors in the pathogenesis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Sep;110:109070. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109070. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35978514 Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of DAZZEON αSleep® Far-Infrared Blanket on Sleep, Blood Pressure, Vascular Health, Muscle Function, Inflammation, and Fatigue.Clocks Sleep. 2024 Sep 4;6(3):499-516. doi: 10.3390/clockssleep6030033. Clocks Sleep. 2024. PMID: 39311228 Free PMC article.
-
Disease-Modifying Effects of Non-Invasive Electroceuticals on β-Amyloid Plaques and Tau Tangles for Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 30;24(1):679. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010679. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photobiomodulation modulates mitochondrial energy metabolism and ameliorates neurological damage in an APP/PS1 mousmodel of Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Apr 5;17(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01714-w. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40188044 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of the sunlight exposure questionnaire.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 14;12:1281301. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1281301. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38550315 Free PMC article.
-
Far-Infrared Irradiation Decreases Proliferation in Basal and PDGF-Stimulated VSMCs Through AMPK-Mediated Inhibition of mTOR/p70S6K Signaling Axis.J Korean Med Sci. 2023 Oct 23;38(41):e335. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2023.38.e335. J Korean Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37873631 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

