Comparison of Eclipse Smart Segmentation and MIM Atlas Segment for liver delineation for yttrium-90 selective internal radiation therapy
- PMID: 35702944
- PMCID: PMC9359022
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.13668
Comparison of Eclipse Smart Segmentation and MIM Atlas Segment for liver delineation for yttrium-90 selective internal radiation therapy
Abstract
Purpose: The aim was to compare Smart Segmentation of Eclipse treatment planning system and Atlas Segment of MIM software for liver delineation for resin yttrium-90 (Y-90) procedures.
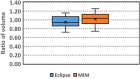
Materials and methods: CT images of 20 patients treated with resin Y-90 selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) were tested. Liver contours generated with Smart Segmentation and Atlas Segment were compared with physician manually delineated contours. Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), mean distance to agreement (MDA), and ratio of volume (RV) were calculated. The contours were evaluated with activity calculations and ratio of activity (RA) was calculated.
Results: Mean DSCs were 0.77 and 0.83, MDAs were 0.88 and 0.71 cm, mean RVs were 0.95 and 1.02, and mean RAs were 1.00 and 1.00, for Eclipse and MIM results, respectively.
Conclusion: MIM outperformed Eclipse in both DSC and MDA, whereas the differences in liver volumes and calculated activities were statistically insignificant between the Eclipse and MIM results. Both auto-segmentation tools can be used to generate initial liver contours for resin Y-90 SIRT, which need to be reviewed and edited by physicians.
Keywords: Eclipse; MIM; auto-segmentation; liver delineation; resin yttrium-90.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of The American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Deep Learning-Based Auto-Segmentation for Liver Yttrium-90 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15330338251327081. doi: 10.1177/15330338251327081. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40152005 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of commercial atlas-based automatic segmentation software for prostate radiotherapy treatment planning.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024 Sep;47(3):881-894. doi: 10.1007/s13246-024-01411-2. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38647633
-
Evaluation of Atlas-based auto-segmentation of liver in MR images for Yttrium-90 selective internal radiation therapy.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023 May;24(5):e13979. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13979. Epub 2023 Apr 17. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 37070130 Free PMC article.
-
Auto-segmentation of low-risk clinical target volume for head and neck radiation therapy.Pract Radiat Oncol. 2014 Jan-Feb;4(1):e31-7. doi: 10.1016/j.prro.2013.03.003. Epub 2013 May 3. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24621429
-
Treatment options for unresectable HCC with a focus on SIRT with Yttrium-90 resin microspheres.Int J Clin Pract. 2017 Nov;71(11). doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12972. Epub 2017 Jul 30. Int J Clin Pract. 2017. PMID: 28758319 Review.
Cited by
-
Prospective deployment of an automated implementation solution for artificial intelligence translation to clinical radiation oncology.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 4;13:1305511. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1305511. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38239639 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetric study on radioembolization with 166Ho poly L-lactic acid microspheres: dead time effects on prediction power.EJNMMI Phys. 2025 Jul 3;12(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s40658-025-00779-8. EJNMMI Phys. 2025. PMID: 40608221 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Auto-Segmentation for Liver Yttrium-90 Selective Internal Radiation Therapy.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jan-Dec;24:15330338251327081. doi: 10.1177/15330338251327081. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40152005 Free PMC article.
-
A deep learning segmentation method to assess dose to organs at risk during breast radiotherapy.Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023 Nov 21;28:100520. doi: 10.1016/j.phro.2023.100520. eCollection 2023 Oct. Phys Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38077272 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of commercial atlas-based automatic segmentation software for prostate radiotherapy treatment planning.Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024 Sep;47(3):881-894. doi: 10.1007/s13246-024-01411-2. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Phys Eng Sci Med. 2024. PMID: 38647633
References
-
- Kennedy A, Nag S, Salem R, et al. Recommendations for radioembolization of hepatic malignancies using Yttrium‐90 microsphere brachytherapy: a consensus panel report from the radioembolization brachytherapy oncology consortium. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68(1):13‐23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

