MicroRNAs: master regulators in host-parasitic protist interactions
- PMID: 35702995
- PMCID: PMC9198802
- DOI: 10.1098/rsob.210395
MicroRNAs: master regulators in host-parasitic protist interactions
Abstract
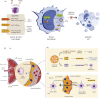
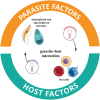
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of small non-coding RNAs present in a wide diversity of organisms. MiRNAs regulate gene expression at a post-transcriptional level through their interaction with the 3' untranslated regions of target mRNAs, inducing translational inhibition or mRNA destabilization and degradation. Thus, miRNAs regulate key biological processes, such as cell death, signal transduction, development, cellular proliferation and differentiation. The dysregulation of miRNAs biogenesis and function is related to the pathogenesis of diseases, including parasite infection. Moreover, during host-parasite interactions, parasites and host miRNAs determine the probability of infection and progression of the disease. The present review is focused on the possible role of miRNAs in the pathogenesis of diseases of clinical interest caused by parasitic protists. In addition, the potential role of miRNAs as targets for the design of drugs and diagnostic and prognostic markers of parasitic diseases is also discussed.
Keywords: apicomplexan; diagnostic and therapeutic tools; host–parasite interactions; kinetoplastids; microrna.
Figures
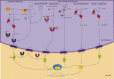

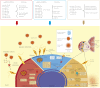
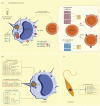
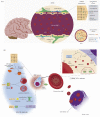

Similar articles
-
microRNAs: Critical Players during Helminth Infections.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 25;11(1):61. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010061. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs in parasitic diseases: potential for diagnosis and targeting.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2012 Dec;186(2):81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 13. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2012. PMID: 23069113 Review.
-
Application of small RNA technology for improved control of parasitic helminths.Vet Parasitol. 2015 Aug 15;212(1-2):47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.06.003. Epub 2015 Jun 9. Vet Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26095949 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulatory microRNAs: promising non-invasive prognostic and diagnostic biomarkers for parasitic infections.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020 Mar;39(3):395-402. doi: 10.1007/s10096-019-03715-8. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31617024 Review.
-
Host-parasite interactions mediated by cross-species microRNAs.Trends Parasitol. 2022 Jun;38(6):478-488. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2022.02.011. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Trends Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35307299 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-read metagenomic sequencing negates inferred loss of cytosine methylation in Myxosporea (Cnidaria: Myxozoa).Gigascience. 2025 Jan 6;14:giaf014. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giaf014. Gigascience. 2025. PMID: 40080648 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of microRNAs and Long Non-Coding RNAs Encoded by Parasitic Helminths in Human Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 25;23(15):8173. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158173. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling the microRNAs Involved in Fasciolosis: Master Regulators of the Host-Parasite Crosstalk.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 29;26(1):204. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010204. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39796061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNAs: Critical Players during Helminth Infections.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 25;11(1):61. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010061. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677353 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryptosporidium parvum regulates HCT-8 cell autophagy to facilitate survival via inhibiting miR-26a and promoting miR-30a expression.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Dec 15;15(1):470. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05606-y. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 36522638 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

