Long-Term Results of Pulmonary Vein Isolation Plus Modified Posterior Wall Debulking Utilizing High-Power Short-Duration Strategy: An All-Comers Study in Real World
- PMID: 35703485
- PMCID: PMC9361222
- DOI: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2022.1631
Long-Term Results of Pulmonary Vein Isolation Plus Modified Posterior Wall Debulking Utilizing High-Power Short-Duration Strategy: An All-Comers Study in Real World
Abstract
Background: High-power short-duration radiofrequency ablation has improved lesion durability in pulmonary vein isolation. In this study, we investigate long-term clinical out-comes of high-power short-duration pulmonary vein isolation and posterior wall debulk- ing as an initial treatment modality in all corner atrial fibrillation patients.
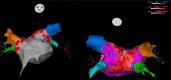
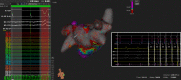
Methods: This is a single-center, retrospective, observational study including all patients who have undergone high-power short-duration pulmonary vein and posterior wall deb-ulking, regardless of atrial fibrillation type and/or duration. High-power short-duration power delivery protocol was defined as 45 W at all ablation sites. Clinical and electrocar-diographic follow-up were performed in all patients.
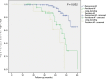
Results: One hundred forty-two patients were enrolled in this study. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation was present in 88 (62%) of patients. The mean follow-up of this study was 36.9 months ± 12.2 months. During the follow-up period, 10 patients (11.4%) with a diag- nosis of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation had recurrence, while recurrence in patients with persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation was slightly higher (15 patients (28.1%) and 5 patients (50%), respectively). No major life-threatening complicationsoccurred.
Conclusion: This study has demonstrated excellent arrhythmia-free outcomes in unselected, real world atrial fibrillation patients undergoing high-power short-duration pulmonary vein and debulking posterior wall isolations, however larger randomized trials are warranted.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: anatomically based circumferential pulmonary vein ablation in combination with a potential-guided segmental approach to achieve complete pulmonary vein isolation.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2011 Jan;30(1):63-72. doi: 10.1007/s10840-010-9533-1. Epub 2011 Jan 21. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2011. PMID: 21253841 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety aspects of very high power very short duration atrial fibrillation ablation using a modified radiofrequency RF-generator: Single-center experience.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022 May;33(5):920-927. doi: 10.1111/jce.15433. Epub 2022 Mar 11. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2022. PMID: 35233883
-
Safety and outcome of very high-power short-duration ablation using 70 W for pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.Europace. 2020 Mar 1;22(3):388-393. doi: 10.1093/europace/euz342. Europace. 2020. PMID: 31872249
-
Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: circumferential pulmonary vein ablation: success rates with and without exclusion of areas adjacent to the esophagus.Clin Res Cardiol. 2017 Sep;106(9):743-751. doi: 10.1007/s00392-017-1118-x. Epub 2017 May 10. Clin Res Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28492985
-
Targeting nonpulmonary vein triggers during atrial fibrillation ablation: is the game worth the candle?Curr Opin Cardiol. 2018 Jan;33(1):50-57. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000469. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29135523 Review.
Cited by
-
Ablation Strategies for Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Beyond the Pulmonary Veins.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 25;13(17):5031. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175031. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274244 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

