Myocardial brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates cardiac bioenergetics through the transcription factor Yin Yang 1
- PMID: 35704040
- PMCID: PMC10226756
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvac096
Myocardial brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates cardiac bioenergetics through the transcription factor Yin Yang 1
Abstract
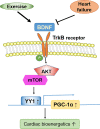
Aims: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is markedly decreased in heart failure patients. Both BDNF and its receptor, tropomyosin-related kinase receptor (TrkB), are expressed in cardiomyocytes; however, the role of myocardial BDNF signalling in cardiac pathophysiology is poorly understood. Here, we investigated the role of BDNF/TrkB signalling in cardiac stress response to exercise and pathological stress.
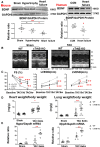
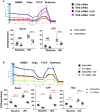
Methods and results: We found that myocardial BDNF expression was increased in mice with swimming exercise but decreased in a mouse heart failure model and human failing hearts. Cardiac-specific TrkB knockout (cTrkB KO) mice displayed a blunted adaptive cardiac response to exercise, with attenuated upregulation of transcription factor networks controlling mitochondrial biogenesis/metabolism, including peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha (PGC-1α). In response to pathological stress (transaortic constriction, TAC), cTrkB KO mice showed an exacerbated heart failure progression. The downregulation of PGC-1α in cTrkB KO mice exposed to exercise or TAC resulted in decreased cardiac energetics. We further unravelled that BDNF induces PGC-1α upregulation and bioenergetics through a novel signalling pathway, the pleiotropic transcription factor Yin Yang 1.
Conclusion: Taken together, our findings suggest that myocardial BDNF plays a critical role in regulating cellular energetics in the cardiac stress response.
Keywords: BDNF; PGC-1α; YY1; cardiac energetics; heart failure.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Figures





References
-
- Lear SA, Hu W, Rangarajan S, Gasevic D, Leong D, Iqbal R, Casanova A, Swaminathan S, Anjana RM, Kumar R, Rosengren A, Wei L, Yang W, Chuangshi W, Huaxing L, Nair S, Diaz R, Swidon H, Gupta R, Mohammadifard N, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Oguz A, Zatonska K, Seron P, Avezum A, Poirier P, Teo K, Yusuf S. The effect of physical activity on mortality and cardiovascular disease in 130 000 people from 17 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries: the PURE study. Lancet 2017;390:2643–2654. - PubMed
-
- Stamatakis E, Gale J, Bauman A, Ekelund U, Hamer M, Ding D. Sitting time, physical activity, and risk of mortality in adults. J Am Coll Cardiol 2019;73:2062–2072. - PubMed
-
- O’Connor CM, Whellan DJ, Lee KL, Keteyian SJ, Cooper LS, Ellis SJ, Leifer ES, Kraus WE, Kitzman DW, Blumenthal JA, Rendall DS, Miller NH, Fleg JL, Schulman KA, McKelvie RS, Zannad F, Pina IL, Investigators H-A. Efficacy and safety of exercise training in patients with chronic heart failure: HF-ACTION randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009;301:1439–1450. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

