Plasma Exchange in a Patient with Immune Thrombocytopenia Associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hospitalized for COVID-19
- PMID: 35704176
- PMCID: PMC9199312
- DOI: 10.1007/s40744-022-00469-2
Plasma Exchange in a Patient with Immune Thrombocytopenia Associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome Hospitalized for COVID-19
Abstract
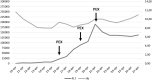
Thrombocytopenia is a common feature of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) and rarely requires treatment. Here we present the case of a 71-year-old man hospitalized for severe immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) secondary to APS and concomitant SARS-CoV-2 infection. The patient was successfully treated with systemic corticosteroids, intravenous immunoglobulins, and plasma exchange (PEX). Few data are published on the use of plasma exchange in the treatment of thrombocytopenia in non-catastrophic APS. In the setting of acute infection when immunosuppressive therapies might be contraindicated, plasma exchange may be considered an effective therapeutic option. SARS-CoV-2 infection may be a trigger for a relapse of immune thrombocytopenia.
Keywords: Lupus anticoagulant; Plasma exchange; SARS-CoV-2; Thrombocytopenia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous