The androgen receptor messenger RNA: what do we know?
- PMID: 35704670
- PMCID: PMC9225383
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2022.2084839
The androgen receptor messenger RNA: what do we know?
Abstract
The Androgen Receptor (AR), transcriptionally activated by its ligands, testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), is widely expressed in cells and tissues, influencing normal biology and disease states. The protein product of the AR gene is involved in the regulation of numerous biological functions, including the development and maintenance of the normal prostate gland and of the cardiovascular, musculoskeletal and immune systems. Androgen signalling, mediated by AR protein, plays a crucial role in the development of prostate cancer (PCa), and is presumed to be involved in other cancers including those of the breast, bladder, liver and kidney. Significant research and reviews have focused on AR protein function; however, inadequate research and literature exist to define the function of AR mRNA in normal and cancer cells. The AR mRNA transcript is nearly 11 Kb long and contains a long 3' untranslated region (UTR), suggesting its biological role in post-transcriptional regulation, consequently affecting the overall functions of both normal and cancer cells. Research has demonstrated that many biological activities, including RNA stability, translation, cellular trafficking and localization, are associated with the 3' UTRs of mRNAs. In this review, we describe the potential role of the AR 3' UTR and summarize RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) that interact with the AR mRNA to regulate post-transcriptional metabolism. We highlight the importance of AR mRNA as a critical modulator of carcinogenesis and its important role in developing therapy-resistant prostate cancer.
Keywords: AR mRNA; Androgen receptor; RNA-binding proteins; prostate cancer; untranslated region.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

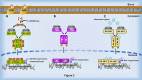
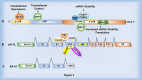
Similar articles
-
Molecular characterization of a novel androgen receptor transgene responsive to MicroRNA mediated post-transcriptional control exerted via 3'-untranslated region.Prostate. 2016 Jun;76(9):834-44. doi: 10.1002/pros.23174. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Prostate. 2016. PMID: 26988939
-
Post-transcriptional regulation of androgen receptor mRNA by an ErbB3 binding protein 1 in prostate cancer.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jun;38(11):3619-31. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq084. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 20159994 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding protein Musashi2 stabilizing androgen receptor drives prostate cancer progression.Cancer Sci. 2020 Feb;111(2):369-382. doi: 10.1111/cas.14280. Epub 2020 Jan 4. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31833612 Free PMC article.
-
Androgen receptor and miR-206 regulation in prostate cancer.Transcription. 2017;8(5):313-327. doi: 10.1080/21541264.2017.1322668. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Transcription. 2017. PMID: 28598253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The androgen receptor mRNA.Bioessays. 2004 Jun;26(6):672-82. doi: 10.1002/bies.20051. Bioessays. 2004. PMID: 15170865 Review.
Cited by
-
Testosterone Exacerbates the Formation of Liver Cancer Induced by Environmental N-Nitrosamines Exposure: Potential Mechanisms and Implications for Human Health.Onco Targets Ther. 2024 May 17;17:395-409. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S456746. eCollection 2024. Onco Targets Ther. 2024. PMID: 38774818 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting androgen receptor stability and degradation: approaches for developing a therapy for spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy.Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jul 17;23(1):344. doi: 10.1186/s12964-025-02351-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40676613 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles and Tunnelling Nanotubes as Mediators of Prostate Cancer Intercellular Communication.Biomolecules. 2024 Dec 27;15(1):23. doi: 10.3390/biom15010023. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39858418 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the effects of androgen deprivation therapy on cadherin switching in advanced prostate cancer: A molecular perspective.Oncol Res. 2023 Jan 12;30(3):137-155. doi: 10.32604/or.2022.026074. eCollection 2022. Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 37305018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role and mechanism of quercetin in improving late-onset hypogonadism through network analysis and experimental validation.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 17. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04022-0. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40090989
References
-
- Stamey TA, Yang N, Hay AR, et al. Prostate-specific antigen as a serum marker for adenocarcinoma of the prostate. N Engl J Med. 1987;317(15):909–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
