Case - Salvage nerve-sparing radical cystectomy for pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma of the bladder
- PMID: 35704935
- PMCID: PMC9665324
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.7915
Case - Salvage nerve-sparing radical cystectomy for pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma of the bladder
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
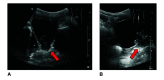
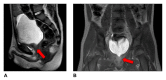
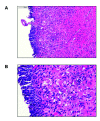
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
