Inflammatory adipose activates a nutritional immunity pathway leading to retinal dysfunction
- PMID: 35705048
- PMCID: PMC9248858
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110942
Inflammatory adipose activates a nutritional immunity pathway leading to retinal dysfunction
Abstract
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the leading cause of irreversible blindness among Americans over 50, is characterized by dysfunction and death of retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells. The RPE accumulates iron in AMD, and iron overload triggers RPE cell death in vitro and in vivo. However, the mechanism of RPE iron accumulation in AMD is unknown. We show that high-fat-diet-induced obesity, a risk factor for AMD, drives systemic and local inflammatory circuits upregulating interleukin-1β (IL-1β). IL-1β upregulates RPE iron importers and downregulates iron exporters, causing iron accumulation, oxidative stress, and dysfunction. We term this maladaptive, chronic activation of a nutritional immunity pathway the cellular iron sequestration response (CISR). RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) analysis of choroid and retina from human donors revealed that hallmarks of this pathway are present in AMD microglia and macrophages. Together, these data suggest that inflamed adipose tissue, through the CISR, can lead to RPE pathology in AMD.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; IL-1β; age-related macular degeneration; high fat diet; iron; macrophage; microglia; neuroinflammation; nutritional immunity; visceral adipose.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
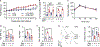
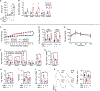
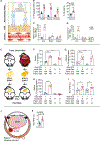

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K08 DK116668/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM125301/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK122099/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F30 EY032339/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY028916/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY015240/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY026012/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY031877/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY001583/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY031209/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY030192/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EY028273/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS105607/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

