Simultaneous quantification of pyrethroid metabolites in urine of non-toilet-trained children in Japan
- PMID: 35705305
- PMCID: PMC9251621
- DOI: 10.1265/ehpm.21-00037
Simultaneous quantification of pyrethroid metabolites in urine of non-toilet-trained children in Japan
Abstract
Background: Pyrethroid (PYR) insecticides are widely used for controlling various pests. There are two types that differ in terms of usage: agricultural-purpose PYR (agriculture-PYR) and hygiene purpose PYR (hygiene-PYRs). Few studies exist on the exposure to these chemicals in small children. In this study, we conducted biomonitoring of urinary pyrethroid metabolites in 1.5-year-old children throughout the year.
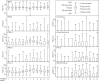
Methods: Study subjects were 1075 children participating in an Aichi regional sub-cohort of the Japan Environment and Children's Study as of 18-month health check-up. The concentrations of four specific hygiene-PYR metabolites including 2,3,5,6-tetrafluoro-1,4-benzenedimethanol (HOCH2-FB-Al), and five common metabolites of hygiene- and agriculture-PYRs including 3-phenoxybenzoic acid (3PBA) and cis- and trans-3-(2,2-dichlorovinyl)-2,2-dimethylcyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (DCCA), were measured in urine samples extracted from soiled diapers using a triple quadrupole gas chromatograph-mass spectrometer.
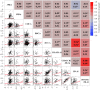
Results: The highest detection frequencies were for 3PBA, followed by DCCA, 1R-trans-chrysanthemum dicarboxylic acid, and HOCH2-FB-Al. Among the six metabolites, urinary concentrations were seasonally varied. However, this variation was not observed in the most studied PYR metabolite, 3PBA. Spearman's correlation analysis demonstrated a significant positive correlation between FB-Al and DCCA (r = 0.56) and HOCH2-FB-Al and 4-methoxymethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrafluorobenzyl alcohol (r = 0.60).
Conclusions: This biomonitoring survey found widespread and seasonally specific exposure to multiple hygiene- and agriculture-PYRs in 1.5-year-old Japanese children.
Keywords: Human biomonitoring; Pyrethroid; Small children; Urine samples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- The Statistics Division of Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://faostat.fao.org/site/424/default. Accessed 10 Sept 2021.
-
- U.S. EPA. Pesticides: Topical & chemical fact sheets; 2002. https://archive.epa.gov/pesticides/regulating/laws/fqpa/web/html/kidpest.... Accessed 10 Nov 2021.

