Principles and methods of global legal epidemiology
- PMID: 35705361
- PMCID: PMC9380495
- DOI: 10.1136/jech-2021-217202
Principles and methods of global legal epidemiology
Abstract
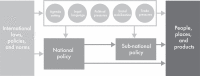
Although the theory and methods of legal epidemiology-the scientific study and deployment of law as a factor in the cause, distribution, and prevention of disease and injury in a population-have been well developed in the context of domestic law, the challenges posed by shifting the frame of analysis to the global legal space have not yet been fully explored. While legal epidemiology rests on the foundational principles that law acts as an intervention, that law can be an object of scientific study and that law has impacts that should be evaluated, its application to the global level requires the recognition that international laws, policies and norms can cause effects independently from their legal implementation within countries. The global legal space blurs distinctions between 'hard' and 'soft' law, often operating through pathways of global agenda setting, legal language, political pressures, social mobilisation and trade pressures to have direct impacts on people, places and products. Despite these complexities, international law has been overwhelmingly studied as operating solely through national policy change, with only one global quasi-experimental evaluation of an international law's impact on health published to date. To promote greater adoption of global legal epidemiology, we expand on an existing typology of public health law studies with examples of policymaking, mapping, implementation, intervention and mechanism studies. Global legal epidemiology holds great promise as a way to produce rigorous and impactful research on the international laws, policies and norms that shape our collective health, equity and well-being.
Keywords: epidemiology; international health; methods; policy; research design.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Mello MM. Peering into hidden worlds: the past and future of legal epidemiology Foreword. Temple Law Rev 2020;92:837–49.
-
- Skuster P. Legal epidemiology for a clearer understanding of abortion laws and their impact. Temple Law Rev 2020;92:917–29.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources