Selection of start codon during mRNA scanning in eukaryotic translation initiation
- PMID: 35705698
- PMCID: PMC9200866
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03534-2
Selection of start codon during mRNA scanning in eukaryotic translation initiation
Abstract
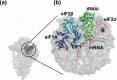
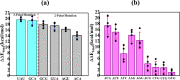
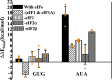
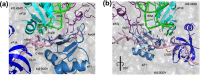
Accurate and high-speed scanning and subsequent selection of the correct start codon are important events in protein synthesis. Eukaryotic mRNAs have long 5' UTRs that are inspected for the presence of a start codon by the ribosomal 48S pre-initiation complex (PIC). However, the conformational state of the 48S PIC required for inspecting every codon is not clearly understood. Here, atomistic molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and energy calculations suggest that the scanning conformation of 48S PIC may reject all but 4 (GUG, CUG, UUG and ACG) of the 63 non-AUG codons, and initiation factor eIF1 is crucial for this discrimination. We provide insights into the possible role of initiation factors eIF1, eIF1A, eIF2α and eIF2β in scanning. Overall, the study highlights how the scanning conformation of ribosomal 48S PIC acts as a coarse selectivity checkpoint for start codon selection and scans long 5' UTRs in eukaryotic mRNAs with accuracy and high speed.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Singh CR. Sequential eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5 (eIF5) binding to the charged disordered segments of eIF4G and eIF2beta stabilizes the 48S preinitiation complex and promotes its shift to the initiation mode. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012;32:3978–3989. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00376-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

