Activation of Dopamine D2 Receptors Alleviates Neuronal Hyperexcitability in the Lateral Entorhinal Cortex via Inhibition of HCN Current in a Rat Model of Chronic Inflammatory Pain
- PMID: 35705785
- PMCID: PMC9468209
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-022-00892-z
Activation of Dopamine D2 Receptors Alleviates Neuronal Hyperexcitability in the Lateral Entorhinal Cortex via Inhibition of HCN Current in a Rat Model of Chronic Inflammatory Pain
Abstract
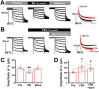
Functional changes in synaptic transmission from the lateral entorhinal cortex to the dentate gyrus (LEC-DG) are considered responsible for the chronification of pain. However, the underlying alterations in fan cells, which are the predominant neurons in the LEC that project to the DG, remain elusive. Here, we investigated possible mechanisms using a rat model of complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced inflammatory pain. We found a substantial increase in hyperpolarization-activated/cyclic nucleotide-gated currents (Ih), which led to the hyperexcitability of LEC fan cells of CFA slices. This phenomenon was attenuated in CFA slices by activating dopamine D2, but not D1, receptors. Chemogenetic activation of the ventral tegmental area -LEC projection had a D2 receptor-dependent analgesic effect. Intra-LEC microinjection of a D2 receptor agonist also suppressed CFA-induced behavioral hypersensitivity, and this effect was attenuated by pre-activation of the Ih. Our findings suggest that down-regulating the excitability of LEC fan cells through activation of the dopamine D2 receptor may be a strategy for treating chronic inflammatory pain.
Keywords: Dopamine D2 receptor; HCN current; Inflammatory pain; Lateral entorhinal cortex; Neuronal hyperexcitability.
© 2022. Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures







References
-
- Boccella S, Cristiano C, Romano R, Iannotta M, Belardo C, Farina A, et al. Ultra-micronized palmitoylethanolamide rescues the cognitive decline-associated loss of neural plasticity in the neuropathic mouse entorhinal cortex-dentate gyrus pathway. Neurobiol Dis. 2019;121:106–119. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.09.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu MG, Lu D, Wang Y, Chen XF, Li Z, Xu Y, et al. Counteracting roles of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes 1 and 5 in regulation of pain-related spatial and temporal synaptic plasticity in rat entorhinal-hippocampal pathways. Neurosci Lett. 2012;507:38–42. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.11.046. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

