Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the SPL gene family and its important role in salt stress in Medicago sativa L
- PMID: 35705909
- PMCID: PMC9199161
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-022-03678-7
Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the SPL gene family and its important role in salt stress in Medicago sativa L
Abstract
Background: SQUAMOSA promoter-binding protein-like (SPL) transcription factors are widely present in plants and are involved in signal transduction, the stress response and development. The SPL gene family has been characterized in several model species, such as A. thaliana and G. max. However, there is no in-depth analysis of the SPL gene family in forage, especially alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.), one of the most important forage crops worldwide.
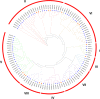
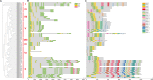
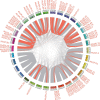
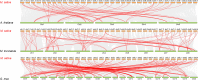
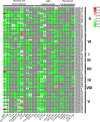
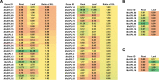
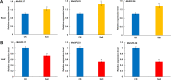
Result: In total, 76 putative MsSPL genes were identified in the alfalfa genome with an uneven distribution. Based on their identity and gene structure, these MsSPLs were divided into eight phylogenetic groups. Seventy-three MsSPL gene pairs arose from segmental duplication events, and the MsSPLs on the four subgenomes of individual chromosomes displayed high collinearity with the corresponding M. truncatula genome. The prediction of the cis-elements in the promoter regions of the MsSPLs detected two copies of ABA (abscisic acid)-responsive elements (ABREs) on average, implying their potential involvement in alfalfa adaptation to adverse environments. The transcriptome sequencing of MsSPLs in roots and leaves revealed that 54 MsSPLs were expressed in both tissues. Upon salt treatment, three MsSPLs (MsSPL17, MsSPL23 and MsSPL36) were significantly regulated, and the transcription level of MsSPL36 in leaves was repressed to 46.6% of the control level.
Conclusion: In this study, based on sequence homology, we identified 76 SPL genes in the alfalfa. The SPLs with high identity shared similar gene structures and motifs. In total, 71.1% (54 of 76) of the MsSPLs were expressed in both roots and leaves, and the majority (74.1%) preferred underground tissues to aerial tissues. MsSPL36 in leaves was significantly repressed under salt stress. These findings provide comprehensive information regarding the SPB-box gene family for improve alfalfa tolerance to high salinity.
Keywords: Legume; Medicago sativa; SPL gene family; Salt stress.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- He F, Kang JM, Zhang F, Long RC, Yang QC. Genetic mapping of leaf-related traits in autotetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Mol Breed. 2019;39(10):147. doi: 10.1007/s11032-019-1046-8. - DOI
-
- Paul D, Lade H. Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria to improve crop growth in saline soils: a review. Agron Sustain Dev. 2014;34(4):737–752. doi: 10.1007/s13593-014-0233-6. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

