FKBP51 mediates resilience to inflammation-induced anxiety through regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 expression in mouse hippocampus
- PMID: 35705957
- PMCID: PMC9198626
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-022-02517-8
FKBP51 mediates resilience to inflammation-induced anxiety through regulation of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 expression in mouse hippocampus
Abstract
Background: Inflammation is a potential risk factor of mental disturbance. FKBP5 that encodes FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51), a negative cochaperone of glucocorticoid receptor (GR), is a stress-inducible gene and has been linked to psychiatric disorders. Yet, the role of FKBP51 in the inflammatory stress-associated mental disturbance remained unclear.
Methods: Fkbp5-deficient (Fkbp5-KO) mice were used to study inflammatory stress by a single intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). The anxiety-like behaviors, neuroimaging, immunofluorescence staining, immunohistochemistry, protein and mRNA expression analysis of inflammation- and neurotransmission-related mediators were evaluated. A dexamethasone drinking model was also applied to examine the effect of Fkbp5-KO in glucocorticoid-induced stress.
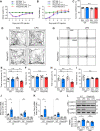
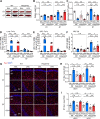
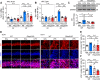
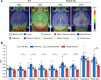
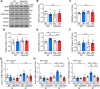
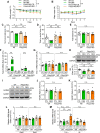
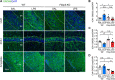
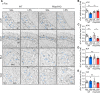
Results: LPS administration induced FKBP51 elevation in the liver and hippocampus accompanied with transient sickness. Notably, Fkbp5-KO but not wild-type (WT) mice showed anxiety-like behaviors 7 days after LPS injection (LPS-D7). LPS challenge rapidly increased peripheral and central immune responses and hippocampal microglial activation followed by a delayed GR upregulation on LPS-D7, and these effects were attenuated in Fkbp5-KO mice. Whole-brain [18F]-FEPPA neuroimaging, which target translocator protein (TSPO) to indicate neuroinflammation, showed that Fkbp5-KO reduced LPS-induced neuroinflammation in various brain regions including hippocampus. Interestingly, LPS elevated glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65), the membrane-associated GABA-synthesizing enzyme, in the hippocampus of WT but not Fkbp5-KO mice on LPS-D7. This FKBP51-dependent GAD65 upregulation was observed in the ventral hippocampal CA1 accompanied by the reduction of c-Fos-indicated neuronal activity, whereas both GAD65 and neuronal activity were reduced in dorsal CA1 in a FKBP51-independent manner. GC-induced anxiety was also examined, which was attenuated in Fkbp5-KO and hippocampal GAD65 expression was unaffected.
Conclusions: These results suggest that FKBP51/FKBP5 is involved in the systemic inflammation-induced neuroinflammation and hippocampal GR activation, which may contribute to the enhancement of GAD65 expression for GABA synthesis in the ventral hippocampus, thereby facilitating resilience to inflammation-induced anxiety.
Keywords: Anxiety; FK506-binding protein 51 (FKBP51); GABA; Glucocorticoid receptor; Glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 (GAD65); Inflammation; Resilience; Ventral hippocampus.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FKBP51 is involved in LPS-induced microglial activation via NF-κB signaling to mediate neuroinflammation.Life Sci. 2024 Aug 15;351:122867. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122867. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38914303
-
Reducing FKBP51 Expression in the Ventral Hippocampus Decreases Auditory Fear Conditioning in Male Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7097. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137097. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000204 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of FKBP5 Affects Neuron Synaptic Plasticity: An Electrophysiology Insight.Neuroscience. 2019 Mar 15;402:23-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2019.01.021. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Neuroscience. 2019. PMID: 30685540
-
The GAD65 knock out mouse - a model for GABAergic processes in fear- and stress-induced psychopathology.Genes Brain Behav. 2015 Jan;14(1):37-45. doi: 10.1111/gbb.12188. Genes Brain Behav. 2015. PMID: 25470336 Review.
-
Hsp90 and FKBP51: complex regulators of psychiatric diseases.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018 Jan 19;373(1738):20160532. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0532. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29203717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CSF proteomics identifies early changes in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease.Cell. 2024 Oct 31;187(22):6309-6326.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.049. Epub 2024 Sep 26. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39332414 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoids, their uses, sexual dimorphisms, and diseases: new concepts, mechanisms, and discoveries.Physiol Rev. 2024 Jan 1;104(1):473-532. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2023. Epub 2023 Sep 21. Physiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37732829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early-life obesogenic environment integrates immunometabolic and epigenetic signatures governing neuroinflammation.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Oct 2;42:100879. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100879. eCollection 2024 Dec. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 39430879 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP5 Induces Senescence in BMSCs and Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation Through the Canonical WNT/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway in Senile Osteoporosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Apr;29(8):e70552. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70552. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40254776 Free PMC article.
-
Intranasal delivery of small extracellular vesicles reduces the progress of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and the overactivation of complement-coagulation cascade and NF-ĸB signaling in SOD1G93A mice.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Aug 22;22(1):503. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02764-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39174972 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

