Comparison of decomposition algorithms for identification of single motor units in ultrafast ultrasound image sequences of low force voluntary skeletal muscle contractions
- PMID: 35705997
- PMCID: PMC9202224
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-022-06093-1
Comparison of decomposition algorithms for identification of single motor units in ultrafast ultrasound image sequences of low force voluntary skeletal muscle contractions
Abstract
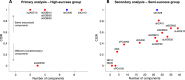
Objective: In this study, the aim was to compare the performance of four spatiotemporal decomposition algorithms (stICA, stJADE, stSOBI, and sPCA) and parameters for identifying single motor units in human skeletal muscle under voluntary isometric contractions in ultrafast ultrasound image sequences as an extension of a previous study. The performance was quantified using two measures: (1) the similarity of components' temporal characteristics against gold standard needle electromyography recordings and (2) the agreement of detected sets of components between the different algorithms.
Results: We found that out of these four algorithms, no algorithm significantly improved the motor unit identification success compared to stICA using spatial information, which was the best together with stSOBI using either spatial or temporal information. Moreover, there was a strong agreement of detected sets of components between the different algorithms. However, stJADE (using temporal information) provided with complementary successful detections. These results suggest that the choice of decomposition algorithm is not critical, but there may be a methodological improvement potential to detect more motor units.
Keywords: Blind source separation; Concentric needle electromyography; Decomposition algorithms; Motor units; Ultrafast ultrasound.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hyvärinen A, Karhunen J, Oja E. Independent component analysis. New York: Wiley; 2001.
-
- Zou H, Hastie T, Tibshirani R. Sparse principal component analysis. J Comput Graph Stat. 2006;15:265–286. doi: 10.1198/106186006X113430. - DOI
-
- Theis FJ, Gruber P, Keck IR, Meyer-Bäse A, Lang EW, Spatiotemporal blind source separation using double-sided approximate joint diagonalization. In, 13th European Signal Processing Conference. IEEE. 2005;2005:1–4.
-
- Belouchrani A, Abed-Meraim K, Cardoso JF, Moulines E. Proc int conf digital signal processing. Princeton: Citeseer; 1993. Second-order blind separation of temporally correlated sources; pp. 346–51.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

