SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human brain microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 35705998
- PMCID: PMC9198209
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-022-02514-x
SARS-CoV-2 productively infects human brain microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
Background: The emergence of the novel, pathogenic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has caused a global health emergency. SARS-CoV-2 is highly contagious and has a high mortality rate in severe patients. However, there is very limited information on the effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection on the integrity of the blood-brain barrier (BBB).
Methods: RNA-sequencing profiling was performed to analyze the transcriptomic changes in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (hBMECs) after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Bioinformatic tools were used for differential analysis. Immunofluorescence, real-time quantitative PCR, and Western blotting analysis were used to explore biological phenotypes.
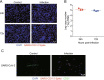
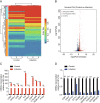
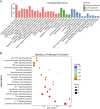
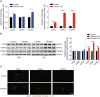
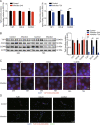
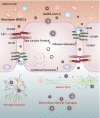
Results: A total of 927 differentially expressed genes were identified, 610 of which were significantly upregulated while the remaining 317 were downregulated. We verified the significant induction of cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules in hBMECs by SARS-CoV-2, suggesting an activation of the vascular endothelium in brain. Moreover, we demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 infection could increase the BBB permeability, by downregulating as well as remodeling the intercellular tight junction proteins.
Conclusions: Our findings demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 infection can cause BBB dysfunction, providing novel insights into the understanding of SARS-CoV-2 neuropathogenesis. Moreover, this finding shall constitute a new approach for future prevention and treatment of SARS-CoV-2-induced CNS infection.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Human brain microvascular endothelial cells; Inflammatory response; Permeability; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2021YDF1800405/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2021YDF1800800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 32102749/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 32122086/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020FCA046/Emergency Science and Technology Project of Hubei Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

