Social, Economic, Technological, and Environmental Factors Affecting Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Thematic Analysis
- PMID: 35706860
- PMCID: PMC9188896
- DOI: 10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_105_20
Social, Economic, Technological, and Environmental Factors Affecting Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Thematic Analysis
Abstract
Background: Today, cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of mortality in both sexes. There are several risk factors for heart diseases; some controllable, others not. However, socioeconomic, technological, and environmental factors can impact CVD as well as exclusive risk factors. Accurate identification and assessment of these factors are often difficult. In the present systematic review, we aimed to explore factors affecting CVD.
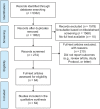
Methods: Multiple databases (MEDLINE, Scopus, ISI Web of Science, and Cochrane) and gray literature were searched. The included studies described at least one determinant of CVD. The framework method was applied to analyze the qualitative data.
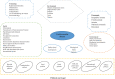
Results: A total of 64 studies from 26 countries were included. The contextual determinants of CVD were categorized into 45 determinants, 15 factors, and 4 main social, economic, technological, and environmental categories. The 15 potentially reversible factors were identified as sociodemographic, violence, smoking, occupation, positive childhood experience, social inequalities, psychological distress, eating habits, neighborhood, family income, rapid technology, environmental pollution, living environments, noise, and disaster.
Conclusions: Devolution and more efficient health policies are required to achieve further sustained reduction in CVD mortality, increase life expectancy, and reduce its associated risk factors. Policymakers should fully address the value of social, economic, technological, and environmental factors. In fact, a prevention agenda should be developed and updated collaboratively in terms of the determinant factors.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; economic; environmental; health system; social; technology.
Copyright: © 2022 International Journal of Preventive Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gakidou E, Afshin A, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1345–422. - PMC - PubMed
-
- James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–858. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–88. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abbafati C, Abbas KM, Abd-Allah F, et al. Global, regional, and national under-5 mortality, adult mortality, age-specific mortality, and life expectancy, 1970–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1084–150. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources