High Expression of PDLIM2 Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Prostate Cancer and Is Correlated with Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Immune Cell Infiltration
- PMID: 35707002
- PMCID: PMC9192325
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2922832
High Expression of PDLIM2 Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Prostate Cancer and Is Correlated with Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Immune Cell Infiltration
Abstract
Purpose: To elucidate the clinical and prognostic role of PDZ and LIM domain protein (PDLIM) genes and the association to epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and immune cell infiltration in patients with prostate cancer (PRAD).
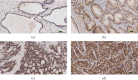
Methods: The data of RNA-seq, DNA methylation, and clinical features of PRAD patients were collected from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database to define the prognostic value of PDLIM gene expression and the association with EMT and immune cell infiltration. A tissue microarray including 134 radical prostatectomy specimens was served as validation by immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining analysis.
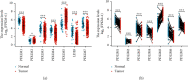
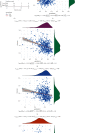
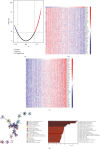
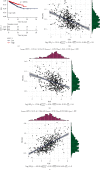
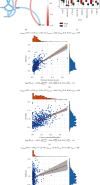
Results: The mRNA levels of PDLIM1/2/3/4/6/7 were significantly downregulated, while PDLIM5 was upregulated in PRAD (P < 0.05). High expression of PDLIM2 mRNA suggests poor progression free interval in PRAD patients. DNA methylation of PDLIM2 was correlated with its mRNA expression level, and that the cg22973076 methylation site in PDLIM2 was associated with shorter PFI (P < 0.05) in PRAD. Single-sample gene-set enrichment and gene functional enrichment results showed that PDLIM2 was correlated with EMT and immune processes. Spearman's test showed a significant correlation with six reported EMT signatures and several EMT signature-related genes. Tumor microenvironment analysis revealed that the PDLIM2 mRNA expression was positively correlated with the immune score, stromal score, and various tumor infiltrating immune cells. Additionally, the results showed that patients in the high-PDLIM2 mRNA expression group may be more sensitive to immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Finally, IHC analysis further implicated the protein level of PDLIM2 was upregulated in PRAD and acts as a novel potential biomarker in predicting tumor progression.
Conclusion: Our study suggests that PDLIM family genes might be significantly correlated with oncogenesis and the progression of PRAD. PDLIM2 correlated with EMT and immune cell infiltration by acting as an oncogene in PRAD, which may serve as a potential prognostic biomarker for PRAD patients.
Copyright © 2022 Songzhe Piao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Integrating single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data unveils antigen presentation and process-related CAFS and establishes a predictive signature in prostate cancer.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 14;22(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04807-y. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38221616 Free PMC article.
-
Immune infiltration phenotypes of prostate adenocarcinoma and their clinical implications.Cancer Med. 2021 Aug;10(15):5358-5374. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4063. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34128342 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic evaluation of the prognostic and immunological role of PDLIM2 across 33 cancer types.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 4;12(1):1933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05987-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35121770 Free PMC article.
-
[PDLIM2 and Its Role in Oncogenesis--Tumor Suppressor or Oncoprote?].Klin Onkol. 2015;28 Suppl 2:2S40-6. doi: 10.14735/amko20152s40. Klin Onkol. 2015. PMID: 26374157 Review. Czech.
-
PDLIM2: Signaling pathways and functions in cancer suppression and host immunity.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Dec;1876(2):188630. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2021.188630. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34571051 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor promoting effect of PDLIM2 downregulation involves mitochondrial ROS, oncometabolite accumulations and HIF-1α activation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 17;43(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03094-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38880883 Free PMC article.
-
PDLIM3 Regulates Migration and Invasion of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma via YAP-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 28;26(7):3147. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073147. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243891 Free PMC article.
-
PDLIM2 is highly expressed in Breast Cancer tumour-associated macrophages and is required for M2 macrophage polarization.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 30;12:1028959. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1028959. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531051 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analyses and Immunophenotyping of LIM Domain Family Genes in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 24;24(5):4524. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054524. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901953 Free PMC article.
-
PDZ and LIM Domain-Encoding Genes: Their Role in Cancer Development.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;15(20):5042. doi: 10.3390/cancers15205042. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lou Y., Diao L., Cuentas E. R. P., et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition is associated with a distinct tumor microenvironment including elevation of inflammatory signals and multiple immune checkpoints in lung adenocarcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research . 2016;22(14):3630–3642. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1434. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mak M. P., Tong P., Diao L., et al. A patient-derived, pan-cancer EMT signature identifies global molecular alterations and immune target enrichment following epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Clinical Cancer Research . 2016;22(3):609–620. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0876. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

