Repeated Exposure of Escherichia coli to High Ciprofloxacin Concentrations Selects gyrB Mutants That Show Fluoroquinolone-Specific Hyperpersistence
- PMID: 35707170
- PMCID: PMC9189390
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.908296
Repeated Exposure of Escherichia coli to High Ciprofloxacin Concentrations Selects gyrB Mutants That Show Fluoroquinolone-Specific Hyperpersistence
Abstract
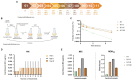
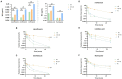
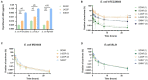
Recent studies have shown that not only resistance, but also tolerance/persistence levels can evolve rapidly in bacteria exposed to repeated antibiotic treatments. We used in vitro evolution to assess whether tolerant/hyperpersistent Escherichia coli ATCC25922 mutants could be selected under repeated exposure to a high ciprofloxacin concentration. Among two out of three independent evolution lines, we observed the emergence of gyrB mutants showing an hyperpersistence phenotype specific to fluoroquinolones, but no significant MIC increase. The identified mutation gives rise to a L422P substitution in GyrB, that is, outside of the canonical GyrB QRDR. Our results indicate that mutations in overlooked regions of quinolone target genes may impair the efficacy of treatments via an increase of persistence rather than resistance level, and support the idea that, in addition to resistance, phenotypes of tolerance/persistence of infectious bacterial strains should receive considerations in the choice of antibiotic therapies.
Keywords: DNA gyrase; experimental evolution; persisters; quinolones; tolerance.
Copyright © 2022 Perault, Turlan, Eynard, Vallé, Bousquet-Melou and Giraud.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

