Comparison of Effectiveness of Home-Based Verses Supervised Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise in Women with Urinary Incontinence
- PMID: 35707300
- PMCID: PMC9190959
- DOI: 10.4103/jmh.jmh_83_21
Comparison of Effectiveness of Home-Based Verses Supervised Pelvic Floor Muscle Exercise in Women with Urinary Incontinence
Abstract
Background: Urinary incontinence (UI) is a significant health problem with serious physical, psychological, and social consequences. Pelvic floor muscle exercise (PFME) is proven efficacious in the prevention and management of UI. A lack of trained physiotherapist in rural areas mars the uptake of physiotherapy and therefore innovative mechanisms are required. The present study was undertaken to evaluate the usefulness of home-based physiotherapy in the management of UI.
Materials and methods: A total of 49 women, who screened positive for UI from a larger study conducted in 4 randomly selected villages of Charutar region, were included in the study. They were assigned home-based or supervised regimens randomly. All participants received education about UI and its management. A structured PFME schedule was developed. Participants in the supervised group received PFME by a trained physiotherapist, while those in the home-based group received training on exercise. Details of each session were documented through a daily diary in both groups. Revised urinary incontinence scale (RUIS) and incontinence impact questionnaire (IIQ-7) were administered at baseline and after 6 months to assess and compare the impact across groups.
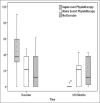
Results: Analysis of variance (with post hoc comparisons) was employed to compare the effect of physiotherapy across groups. Only 18 (10 supervised and 8 home-based group) out of 49 women participated. Another 10 provided the required data, albeit had not done any exercises. The mean standard deviation of RUIS (P = 0.84) and IIQ-7 (P = 0.55) scores was similar at baseline across the groups. The RUIS (P = 0.01) and IIQ-7 (P = 0.006) improved significantly; however, post hoc analysis revealed that both RUIS and IIQ-7 improved significantly only in the supervised group.
Conclusion: Supervised exercise worked better, whereas home-based exercise failed to achieve the desired impact. Identifying barriers in home-based exercise and finding feasible solutions would prove a breakthrough in the management of UI in resource-limited settings.
Keywords: Physiotherapy; randomized control trial; urinary incontinence.
Copyright: © 2022 Journal of Mid-life Health.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report: 1999: Making a Difference. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 1999. [Last accessed on 2018 Apr 01]. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/ handle/10665/42167/WHR_1999.pdf .
-
- Minassian VA, Drutz HP, Al-Badr A. Urinary incontinence as a worldwide problem. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2003;82:327–38. - PubMed
-
- Trantafylidis SC. Impact of urinary incontinence on quality of life. Pelviperineology. 2009;28:51–3.
-
- Bedretdinova D, Fritel X, Panjo H, Ringa V. Prevalence of female urinary incontinence in the general population according to different definitions and study designs. Eur Urol. 2016;69:256–64. - PubMed
-
- Jokhio AH, Rizvi RM, Rizvi J, MacArthur C. Urinary incontinence in women in rural Pakistan: Prevalence, severity, associated factors and impact on life. BJOG. 2013;120:180–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous