Modern Diagnostic Imaging Technique Applications and Risk Factors in the Medical Field: A Review
- PMID: 35707373
- PMCID: PMC9192206
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5164970
Modern Diagnostic Imaging Technique Applications and Risk Factors in the Medical Field: A Review
Abstract
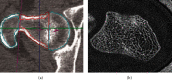
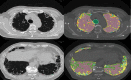
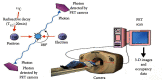
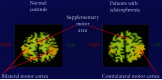
Medical imaging is the process of visual representation of different tissues and organs of the human body to monitor the normal and abnormal anatomy and physiology of the body. There are many medical imaging techniques used for this purpose such as X-ray, computed tomography (CT), positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), digital mammography, and diagnostic sonography. These advanced medical imaging techniques have many applications in the diagnosis of myocardial diseases, cancer of different tissues, neurological disorders, congenital heart disease, abdominal illnesses, complex bone fractures, and other serious medical conditions. There are benefits as well as some risks to every imaging technique. There are some steps for minimizing the radiation exposure risks from imaging techniques. Advance medical imaging modalities such as PET/CT hybrid, three-dimensional ultrasound computed tomography (3D USCT), and simultaneous PET/MRI give high resolution, better reliability, and safety to diagnose, treat, and manage complex patient abnormalities. These techniques ensure the production of new accurate imaging tools with improving resolution, sensitivity, and specificity. In the future, with mounting innovations and advancements in technology systems, the medical diagnostic field will become a field of regular measurement of various complex diseases and will provide healthcare solutions.
Copyright © 2022 Shah Hussain et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures







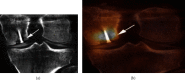

References
-
- Laal M. Innovation process in medical imaging. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences . 2013;81:60–64. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.06.388. - DOI
-
- Kasban H., El-Bendary M. A. M., Salama D. H. A comparative study of medical imaging techniques. International Journal of Information Science and Intelligent System . 2015;4(2):37–58.
-
- National Research Council. Mathematics and Physics of Emerging Biomedical Imaging . National Academies Press; 1996. - PubMed
-
- Flower M. A. Webb's Physics of Medical Imaging . CRC Press; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

