Neurotrophic Keratopathy in Systemic Diseases: A Case Series on Patients Treated With rh-NGF
- PMID: 35707524
- PMCID: PMC9189296
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.920688
Neurotrophic Keratopathy in Systemic Diseases: A Case Series on Patients Treated With rh-NGF
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the prevalence, clinical ocular presentation and corneal healing in moderate and severe neurotrophic keratopathy (NK) caused by systemic diseases and treated with rh-NGF.
Setting: Department of Biomedical and Dental Sciences and Morphofunctional Imaging, Ophthalmology Clinic, University of Messina, Italy.
Design: Retrospective observational study of case series.
Materials and methods: In this retrospective observational study 11 patients (five female and six males) aged from 24 to 88 years (55.4 ± 21.3 years) with moderate and severe NK caused by systemic diseases were enrolled. The VAS questionnaire was dispensed. The ocular examination comprised slit lamp evaluation, ocular surface assessment with Keratograph 5M (Oculus, Germany), corneal sensitivity with Cochet-Bonnet esthesiometer (Lunneaux, France) and corneal thickness measurement with AC-OCT (DRI, Triton, Topcon, Japan). The underlying systemic causes of NK were determined.
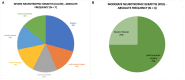
Results: The main cause of NK was post-neuroma surgery (36%), followed by diabetes (18%). The remaining causes were rheumatoid arthritis (9%), post-traumatic (9%), post-surgery (9%), atopia (9%), Graves' disease (9%). Seven eyes presented severe grade of NK with corneal ulcer and in four a moderate grade was registered. The rh-NGF (Cenegermin) was administered with a standard protocol one drop six times daily for 8 weeks. The complete healing of all corneal defects was registered at the end of the treatment.
Conclusions: The post-neuroma surgery was the most common cause of NK and severe grade was clinically more represented. The rh-NGF proved effective to promote corneal recovery with all defects healed after the treatment.
Keywords: Cenegermin; nerve growing factor; neurotrophic keratitis; neurotrophic keratopathy; rh-NGF.
Copyright © 2022 Meduri, Oliverio, Valastro, Azzaro, Camellin, Franchina, Inferrera, Roszkowska and Aragona.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The use of rh-NGF in the management of neurotrophic keratopathy.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 8;4:1408587. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1408587. eCollection 2024. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39040985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical and instrumental assessment of the corneal healing in moderate and severe neurotrophic keratopathy treated with rh-NGF (Cenegermin).Eur J Ophthalmol. 2022 Nov;32(6):3402-3410. doi: 10.1177/11206721221097584. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35473440
-
The Role of Hi-Tech Devices in Assessment of Corneal Healing in Patients with Neurotrophic Keratopathy.J Clin Med. 2022 Mar 14;11(6):1602. doi: 10.3390/jcm11061602. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35329927 Free PMC article.
-
Eight months follow-up of corneal nerves and sensitivity after treatment with cenegermin for neurotrophic keratopathy.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Feb 21;17(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02237-5. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 35189948 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular basis of neurotrophic keratopathy: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. A review.Ocul Surf. 2021 Jan;19:224-240. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2020.09.007. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Ocul Surf. 2021. PMID: 33022412 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Topical Azithromycin versus Systemic Doxycycline in Treatment of Meibomian Gland Dysfunction.J Ophthalmol. 2023 Aug 8;2023:4182787. doi: 10.1155/2023/4182787. eCollection 2023. J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37588518 Free PMC article.
-
The use of rh-NGF in the management of neurotrophic keratopathy.Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 8;4:1408587. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1408587. eCollection 2024. Front Ophthalmol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39040985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Feroze K, Patel B. StatPearls. (2019). Available online at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431106/ (accessed November 2, 2021).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources