Delay discounting and alcohol consumption correlate with dorsal anterior insula activation during choice in nontreatment-seeking heavy drinkers
- PMID: 35707988
- PMCID: PMC9427725
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.14888
Delay discounting and alcohol consumption correlate with dorsal anterior insula activation during choice in nontreatment-seeking heavy drinkers
Abstract
Background: The anterior insular cortex (AIC), a prominent salience network node, integrates interoceptive information and emotional states into decision making. While AIC activation during delay discounting (DD) in alcohol use disorder (AUD) has been previously reported, the associations between AIC activation, impulsive choice, alcohol consumption, and connectivity remain unknown. We therefore tested AIC brain responses during DD in heavy drinkers and their association with DD performance, alcohol drinking, and task-based connectivity.
Methods: Twenty-nine heavy drinkers (12 females; mean (SD) age=31.5 ± 6.1 years; mean (SD)=40.8 ± 23.4 drinks/week) completed a DD task during functional MRI. Regions activated during DD decision making were tested for correlation with DD behavior and alcohol drinking. Psychophysiological interaction (PPI) models assessed the task-dependent functional connectivity (FC) of activation during choice.
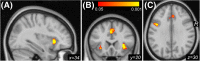
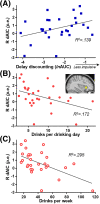
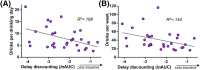
Results: Delay discounting choice activated bilateral anterior insular cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and left precentral gyrus. Right dorsal (d) AIC activation during choice negatively correlated withdiscounting of delayed rewards and alcohol consumption. PPI analysis revealed FC of the right dAIC to both the anterior and posterior cingulate cortices-key nodes in the midline default mode network.
Conclusions: Greater dAIC involvement in intertemporal choice may confer more adaptive behavior (lower impulsivity and alcohol consumption). Moreover, salience network processes governing discounting may require midline default mode (precuneus/posterior cingulate cortex) recruitment. These findings supporta key adaptive role for right dAIC in decision making involving future rewards and risky drinking.
Keywords: alcohol use disorder; alcoholism; monetary discounting; psychophysiological interaction; task fMRI.
© 2022 The Authors. Alcoholism: Clinical & Experimental Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Research Society on Alcoholism.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

